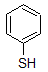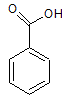|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
A membrane permeable only to water is placed between solutions A and B. Solution A contains 3 mM glucose and solution B contains 3 mM NaCl. In which direction will the water flow? |
|
A
|
from A to B |
B
|
from B to A |
C
|
neither; there are 3 mM of solute in both solutions |
D
|
neither; there is no force to drive the water in either direction |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
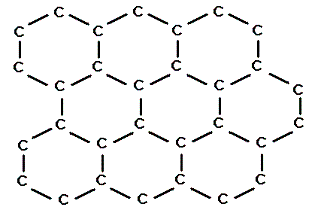
Arrange the following compounds in order of increasing solubility in ethanol.
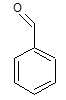
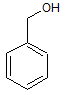
I.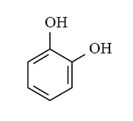
II.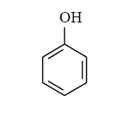
III.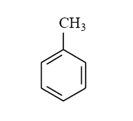
|
|
A
|
I < II < III |
B
|
II < I < III |
C
|
III < I < II |
D
|
III < II < I |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Alcohols | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
In the mixed-melting point analysis of an unknown sample, a pure standard of triphenylmethanol is added. If the unknown sample is in fact benzophenone, which of the following is the most likely result of the analysis? |
|
A
|
The melting point of the mixed samples will be higher than the melting point of the unknown alone. |
B
|
The melting point of the mixed samples will be lower than the melting point of the unknown alone. |
C
|
The melting point of the mixed samples will be the same as the melting point of the unknown alone. |
D
|
The melting point of the mixed samples cannot be predicted based on the information given. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
An oil consisting of high molecular weight hydrocarbons is present in a sample of waste water. Which of the following solvents would be the best extraction solvent for the oil? |
|
A
|
methanol |
B
|
acetone |
C
|
hexane |
D
|
diethyl ether |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
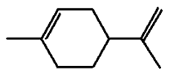
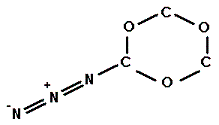
Into which solvent would the following compound most easily dissolve?
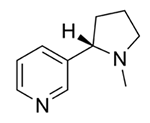 |
|
A
|
methanol |
B
|
water |
C
|
CCl4 |
D
|
hexane |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
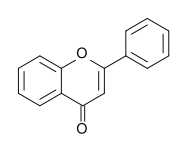
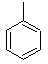
Into which solvent would the following compound most easily dissolve?
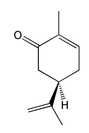 |
|
A
|
acetone |
B
|
water |
C
|
hexane |
D
|
H2O2
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following decreases the solubility of a solute in solution? |
|
A
|
adding the solute in a large, solid chunk rather than finely ground particles |
B
|
increasing the pressure above the surface of the solution |
C
|
adding another solute to the solution |
D
|
lowering the temperature |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
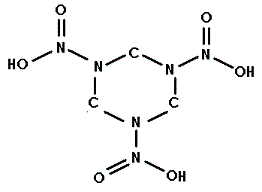
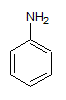
Into which solvent would the following compound most easily dissolve?
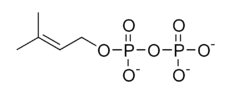 |
|
A
|
water |
B
|
ether |
C
|
CCl4 |
D
|
acetone |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
A solute is placed inside of a solvent. It is noted that the solute has very strong attractive forces with the solvent. In a plot of Gibbs free energy versus temperature, what can be inferred about the y-intercept of the graph of the pure solvent and the solvent with solute? |
|
A
|
The pure solvent will intersect the y-intercept lower than the impure solvent. |
B
|
The pure solvent will intersect the y-intercept higher than the impure solvent. |
C
|
The pure solvent will intersect the y-intercept at the same level as the impure solvent. |
D
|
There is not enough information to tell. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Thermochemistry | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
CO2 dissolves in water. Once dissolved, |
|
A
|
it decreases the pH of the solution due to formation of HCO2 + OH- |
B
|
it decreases the pH of the solution due to formation of HCO3 + H+ |
C
|
it increases the pH of the solution due to formation of HCO2 + OH- |
D
|
it increases the pH of the solution due to formation of HCO3 + H+ |
|
|
|
Tags:
Acid/Base Equilibria | Solutions | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
When 1000 mL of 100% methanol is mixed with 1000 mL of water, less than 1950 mL of liquid results. This is most likely due to |
|
A
|
evaporation of some of both of the liquids prior to mixing |
B
|
evaporation of the solution after mixing, a process which increases the temperature of the solution |
C
|
cooling of the solution due to mixing, resulting in a denser solution with less volume |
D
|
adjustment of the hydrogen bonding of the liquids, resulting in a denser solution and hence, a smaller volume |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
A compound is insoluble in all of the following solvents:
Diethyl Ether
Ethanol
Methanol
Water
Benzene
Tetrahydrofuran
Chloroform
What is the most likely identity of the compound?
|
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
During atomic absorption spetroscopy, the concentration of certain atoms can be measured in very low concentrations. The absorption is tuned to the optimal absorption wavelength of individual metals. Will atomic absorption spectroscopy be useful for the measurement of ethanol in pure water? |
|
A
|
Yes because a mixture of ethanol and water does not have metal ions |
B
|
Yes because ethanol and water mixtures contain metal ions |
C
|
No because a mixture of ethanol and water does not have metal ions |
D
|
No because ethanol and water mixtures contain metal ions |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electromagnetics | Solutions | Alcohols | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which solution is the most concentrated? |
|
A
|
1 mole of solute dissolved in 1 liter of solution? |
B
|
2 moles of solute dissolved in 3 liters of solution? |
C
|
6 moles of solute dissolved in 4 liters of solution? |
D
|
4 moles of solute dissolved in 8 liters of solution? |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
After a chemical extraction you are unsure about whether you have any chloride ions in your solution. Which is the best option for testing the presence of chloride in your solution?
|
|
A
|
Sodium Nitrate |
B
|
Silver Nitrate |
C
|
Iron Sulfate |
D
|
Ammonium Sulfate |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Separation and Purification | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
Imagine a solution of polyaspartyl peptides in water. You mix dilute CaCl2 into the solution. What will be the consequence of this action? |
|
A
|
The polyaspartyl peptides will precipitate |
B
|
The polyaspartyl residues will hydrolyze to free amino acids |
C
|
The CaCl2 will precipitate |
D
|
The pH of the solution will decrease |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which procedure will increases the solubility of KCl in water? |
|
A
|
stirring the solute and solvent mixture |
B
|
increasing the surface area of the solute |
C
|
raising the temperature of the solvent |
D
|
increasing the pressure on the surface of the solvent |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 20 |
Go |
Q:
|
Large macromolecules have varying solubility in water. Their ability to dissolve is dependent mainly on |
|
A
|
their ability to hydrogen bond with water |
B
|
their ability to hydrogen bond with one another |
C
|
their ability to repel water |
D
|
their ability to repel one another |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following substances in water will act as the strongest electrolyte? Assume 1 mol of each is mixed into 1 L of water. |
|
A
|
AgCl |
B
|
NaCl |
C
|
Sucrose |
D
|
O2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular ion, X+, is very harmful to the human body. Which of the following substances would be least harmful if taken orally, given the chemical formulas for the compounds as well as the Ksp values? |
|
A
|
X2S, Ksp=10-21 |
B
|
XCl, Ksp=10-14 |
C
|
XBr, Ksp=10-16 |
D
|
X2S, Ksp=10-23 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 23 |
Go |
Q:
|
Three identical solutions are brought to their cloud point.
Solution 1 is kept at its cloud point and solute is added
Solution 2 is heated above its cloud point
Solution 3 is cooled below its cloud point
If each solution is filtered, which would you expect will have precipitate remain in the filter? |
|
A
|
Solution 1 and 2 |
B
|
Solution 2 only |
C
|
Solution 1 and 3 |
D
|
Solution 3 only |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Separation and Purification | |
|
| 24 |
Go |
Q:
|
The solubility of Mg(OH)2 is equal to z. Which expression is equal to the solubility product for Mg(OH)2? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 25 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the molarity of a solution of KCl with specific gravity 1.007? (Molar mass of KCl is 74.6 g/mol) |
|
A
|
0.06 M |
B
|
0.01 M |
C
|
0.6 M |
D
|
0.1 M |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 26 |
Go |
Q:
|
Organic molecules with a high degree of conjugation typically produce colors in solution. Which of the following also generally produce a colored solution? |
|
A
|
Strong acids and strong bases |
B
|
Elements with p orbitals and no d orbitals |
C
|
Dissolved gases |
D
|
Transition elements |
|
|
|
Tags:
Periodic Table | Solutions | |
|
| 27 |
Go |
Q:
|
A membrane permeable only to water is placed between solutions A and B. Solution A contains 3 mM glucose and solution B contains 3 mM NaCl. In which direction will the water flow? |
|
A
|
from A to B |
B
|
from B to A |
C
|
neither; there are 3 mM of solute in both solutions |
D
|
neither; there is no force to drive the water in either direction |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 28 |
Go |
Q:
|
An experiment is conducted below by saturating water with the various salts in the table below. For each of the salt solutions, the electrical conductivity was measured with the readings below. Pure water prior to the addition of salt had a conductivity reading of less than 0.1 mS/cm.
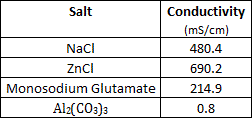
Which of the following is the most likely reason for the low conductivity readings of Al2(CO3)3? |
|
A
|
Aluminum carbonate forms an acidic solution which causes the evolution of carbon dioxide from carbonate, thus removing ions from solution and decreasing the conductivity. |
B
|
Aluminum carbonate ions are unstable in water, and thus do not add significantly to the conductivity of the solution. |
C
|
Aluminum carbonate is insoluble in water and the conductivity readings are a result of very minor dissociation in water. |
D
|
Aluminum carbonate has a net oxidation state of 0, and thus does not add significantly to the conductivity of the solution. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 29 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is most soluble in water? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 30 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is not a colligative property? |
|
A
|
Increased vapor pressure with the addition of a nonvolatile solute to a solution. |
B
|
Increase boiling temperature with the addition of a nonvolatile solute to a solution. |
C
|
Decreased freezing temperature with the addition of solute to a solution. |
D
|
Increased osmotic pressure with the addition of solute to a solution. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 31 |
Go |
Q:
|
Using the table below, which solution would be best suited recrystallization of benzoic acid.
| Solvent |
High Temperature |
Low Temperature |
| Water (pH 7) |
Soluble |
Insoluble |
| Water (pH 12) |
Soluble |
Soluble |
| Solvent X |
Insoluble |
Insoluble |
|
|
A
|
Solvent X |
B
|
Water (pH 7) |
C
|
Water (pH 12) |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined with the given information. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 32 |
Go |
Q:
|
During a purification experiment, Compound X is extracted from ethyl acetate in which it is readily soluble into an aqueous Solution A in which it is only moderately soluble. Compound X has a pKa of 2.8 and has a carboxylic acid as its primary functional group. In the next step, the student wants to precipitate Compound X and attempts different experimental conditions. The observations from two conditions are shown in the table below.
| � |
Condition 1 |
Condition 2 |
| pH |
6.5 |
0.5 |
Assuming the there is no difference in the experimental conditions except for the pH, which of the following is true? |
|
A
|
Condition 1 will precipitate Compound X because Compound X will be insoluble when the pH is above the pKa |
B
|
Condition 2 will precipitate Compound X because Compound X will be insoluble when the pH is below the pKa |
C
|
Condition 1 will precipitate Compound X because Compound X will be insoluble when the pH is below the pKa |
D
|
Condition 2 will precipitate Compound X because Compound X will be insoluble when the pH is above the pKa |
|
|
|
Tags:
Acid/Base Equilibria | Solutions | Carboxylic Acids | |
|
| 33 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which piece of information would be least useful for determining the solubility of an organic compound in water at pH 7? |
|
A
|
molecular weight |
B
|
chemical structure |
C
|
Ksp |
D
|
density |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 34 |
Go |
Q:
|
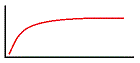
A solute is added to a liquid and forms a solution. The concentration of the solution is measured with respect to the quantity of solute added. Which of the following graphs most closely predicts the expected experimental results? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 35 |
Go |
Q:
|
The vapor pressure of an unknown pure liquid is 28 mmHg. If 4 moles of nonvolatile solute are dissolved into the liquid to form 7 moles of solution, what is the vapor pressure of the solution? |
|
A
|
12 mmHg |
B
|
16 mmHg |
C
|
49 mmHg |
D
|
There is not enough information to determine the answer. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Solutions | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 36 |
Go |
Q:
|
The solubility of various barium salts is shown below. 0.05 mol of each salt is placed into a single solution and excess NaSO4 is added. Which of the salts will be least prevalent in the precipitate after a long time?
| Salt |
Solubility (g/100 mL) |
| BaI2 |
221 |
| BaS |
7.68 |
| Ba(NO3)2 |
4.95 |
| BaSO4 |
2.45 x 10-3 |
|
|
A
|
BaI2 |
B
|
BaS |
C
|
Ba(NO3)2 |
D
|
BaSO4 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 37 |
Go |
Q:
|
Pharmaceutical drugs are often listed as being provided in HCl salt form. These drugs have HCl added to increase the drug solubility by: |
|
A
|
protonating a carboxyl group |
B
|
dehydrating an alcohol |
C
|
protonating an amine group |
D
|
hydrogenating an alkene group |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 38 |
Go |
Q:
|
The precipitation of salts can be improved with which of the following steps? |
|
A
|
Increasing the temperature |
B
|
Adding more water to the solution |
C
|
Decreasing the pressure over the solution |
D
|
Adding ethanol to the solution |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 39 |
Go |
Q:
|
At the critical point of a substance, the liquid state is indistinguishable from the gas, yielding properties of both liquids and gases. For such a fluid of SO2, which of the following would most readily be dissolved? |
|
A
|
KCl |
B
|
NH4OH |
C
|
H3COCH3 |
D
|
NaNO3 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 40 |
Go |
Q:
|
A 1 M solution of glucose in water will have |
|
A
|
a higher boiling point than a 1M NaCl solution |
B
|
the same boiling point as a 1M NaCl solution |
C
|
a lower boiling point than a 1M NaCl solution |
D
|
There is not enough information to answer the question. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 41 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following molecules is amphoteric in a solution? |
|
A
|
Table salt |
B
|
Borane (BH3) |
C
|
Hydrobromic acid |
D
|
Glycine |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 42 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following may hold true of a compound if an increase in pH of the solvent results in increased solubility of the compound? |
|
A
|
The compound is an acid |
B
|
The compound is a base |
C
|
The compound contains an ionic bond |
D
|
The compound has charge at neutral pH |
|
|
|
Tags:
Acid/Base Equilibria | Solutions | |
|
| 43 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds will be most soluble in a 1 M HCl solution? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 44 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following substances is least soluble in water? |
|
A
|
ZnS, Ksp = 2 x 10-25 |
B
|
CuS, Ksp = 8 x 10-37 |
C
|
CdS, Ksp = 1 x 10-27 |
D
|
HgS, Ksp = 8 x 10-53 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 45 |
Go |
Q:
|
Flame atomic absorption spectroscopy (AAS) is a technique used to convert free atoms into their gaseous state and measure the absorption of light. This technique follows the Beer-Lambert law, meaning it is most useful for which of the following? |
|
A
|
Determining the identity of an unknown element in a sample. |
B
|
Determining the concentration of a solution. |
C
|
Identifying the decomposition rate of the element in the solution. |
D
|
Finding the relative solubility of the atom in different solutions. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 46 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following solutions will have the lowest freezing point? |
|
A
|
0.10 M NaCl |
B
|
0.15 M CaCl2 |
C
|
0.20 M EtOH |
D
|
0.15 M CH3COOH |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 47 |
Go |
Q:
|
The quantity of Ba(OH)2 that dissolves in water can be increased with the addition of which of the following? |
|
A
|
NaOH |
B
|
HCl |
C
|
NH4OH |
D
|
NH3 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 48 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is least likely to be soluble in diethyl ether? |
|
A
|
acetone |
B
|
butanol |
C
|
sodium acetate |
D
|
methyl propanoate |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 49 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular solution of a concentrated acid has a pH of 2. The water is evaporated until half the volume remains, leaving the acid twice as concentrated. What has happened to the pH of the solution? |
|
A
|
The pH is equal to or below 1. |
B
|
The pH is between 1 and 2. |
C
|
The pH remains at 2. |
D
|
The pH is between 2 and 4. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Acid/Base Equilibria | Solutions | |
|
| 50 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the molarity of pure ethanol, assuming its density is 0.8 g/mL? |
|
A
|
8 M |
B
|
13.9 M |
C
|
17.4 M |
D
|
21.8 M |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 51 |
Go |
Q:
|
To increase the pH of a solution of a strong acid by 1 point, the solution would need to be diluted by how much? |
|
A
|
a factor of 1 |
B
|
a factor of 2 |
C
|
a factor of 10 |
D
|
a factor of 100 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 52 |
Go |
Q:
|
The first step in converting opium into heroin involves its treatment with Ca(OH)2, which forms a water-soluble compound from an otherwise water-insoluble compound. The purpose of the calcium hydroxide is to form a(n): |
|
A
|
acid |
B
|
base |
C
|
salt |
D
|
hydrophobic compound |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 53 |
Go |
Q:
|
Two solutions are separated by a semipermeable membrane allowing only water to flow through. In one solution, 1 mole of CaCl2 is added while in the other solution, 1 mole of NaCl is added. Water will flow from the NaCl solution into the CaCl2 solution because: |
|
A
|
the calcium ion is larger than the sodium ion. |
B
|
there are more moles of ions in the CaCl2 solution than in the NaCl solution. |
C
|
calcium is divalent while sodium is monovalent. |
D
|
calcium is more electropositive and has a stronger affinity for water. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 54 |
Go |
Q:
|
Boiling food generally takes longer at high altitude than at sea level due to the lowered boiling point at lower atmospheric pressures. The boiling temperature can be brought up to 100 °C by which of the following mechanisms? |
|
A
|
Reducing the amount of water being used at a given time |
B
|
Increasing the amount of heat added by the stove |
C
|
Adding salt to the water |
D
|
Reducing the amount of food solids being cooked at a given time |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 55 |
Go |
Q:
|
A tub of pure water holds a floating craft in the middle. A student slowly adds salt to the tub, increasing the molarity of the tub to 3 M. Which of the following describes what the floating craft will do? Assume the level of the water remains constant. |
|
A
|
The craft will sink deeper into the water. |
B
|
The craft will retain its current level of buoyancy. |
C
|
The craft will rise higher on the water. |
D
|
The craft will sink to the bottom of the tub. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Forces | Solutions | |
|
| 56 |
Go |
Q:
|
MgH2 + 2H2O → 2 H2 + Mg(OH)2
How many moles of MgH2 would need to be decomposed in the reaction above in order to produce 11.2 L of H2 gas at STP? |
|
A
|
1 mole |
B
|
1/4 mole |
C
|
1/2 mole |
D
|
2 moles |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Solutions | |
|
| 57 |
Go |
Q:
|
A student adds 232 grams of NaCl to 2 L of pure water. If the student tries to freeze the mixture, at what temperature will it freeze? (Assume the kf of water is 1.86 °C m-1) |
|
A
|
-8 °C |
B
|
-4 °C |
C
|
4 °C |
D
|
8 °C |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 58 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which is the correct ordering for the following solutions when listed from highest boiling point to lowest boiling point? Note the Ka of HF is 7.2 x 10-4 and the remaining solutes are highly water-soluble.
0.05 m Mg(NO3)2
0.10 m sucrose
0.15 m KCl
0.10 m NaI
0.05 m HF |
|
A
|
Mg(NO3)2, KCl, NaI, HF, sucrose |
B
|
KCl, NaI, Mg(NO3)2, sucrose, HF
|
C
|
NaI, KCl, Mg(NO3)2, sucrose, HF |
D
|
KCl, Mg(NO3)2, NaI, sucrose, HF |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 59 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is the most likely identity of the precipitate formed when KCl(aq) is added to Pb(NO3)2(aq)? |
|
A
|
PbCl |
B
|
Pb2Cl |
C
|
PbCl2 |
D
|
PbCl4 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 60 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following solutions would have the highest boiling point? |
|
A
|
1 M LiCl |
B
|
1 M NaCl |
C
|
1 M KCl |
D
|
All of the above solutions will have the same boiling point. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 61 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular liquid is brought up to boiling point. Some solute (for instance sodium chloride) is added to the solution. Which of the following would hold true? |
|
A
|
The solution will stop boiling |
B
|
The solution will boil more vigorously |
C
|
Vapor pressure of the solution will decrease |
D
|
Temperature will fall |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Solutions | |
|
| 62 |
Go |
Q:
|
Ca(OH)2 has Ksp = 10-6. If 0.1 mol of Ca(OH)2 was added to 1 L of pure water, what would be the approximate pH of the resulting solution? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Acid/Base Equilibria | Solutions | |
|
| 63 |
Go |
Q:
|
400 mL of 0.01M HCl is mixed with 100 mL of 0.1M MgCl2. What is the final molarity of Cl- in the solution? |
|
A
|
0.24 mol/L |
B
|
0.024 mol/L |
C
|
0.048 mol/L |
D
|
0.36 mol/L |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 64 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given a solubility of 30 mmol/L, which of the following salts would have the highest value for its Ksp? |
|
A
|
MX |
B
|
M2SO4 |
C
|
MX5 |
D
|
M3PO4 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 65 |
Go |
Q:
|
A solution contains 1.2 M NaOH. Which of the following dilutions would give a final NaOH concentration of 60 mM? |
|
A
|
20 parts water and 1 part 1.2 M NaOH
|
B
|
1 part 1.2 M NaOH and 9 parts water |
C
|
19 parts water and 1 part 1.2 M NaOH |
D
|
1 part 1.2 M NaOH and 10 parts water |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 66 |
Go |
Q:
|
Certain proteins can be precipitated out of solution by the addition of high concentrations of ionic solutions. This suggests that the proteins in question are: |
|
A
|
largely ionic on their surfaces. |
B
|
largely hydrophobic on their surfaces. |
C
|
very low in molecular weight. |
D
|
very high in molecular weight. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 67 |
Go |
Q:
|
A student prepares a solution of ethanol and adds one equivalent of PBr3 to the mixture. The student extracts the alkyl product and then adds an equivalent of CH3Li to the purified product in solution. What is the final product of the reactions?
|
|
A
|
Propane |
B
|
1-Bromoethanol |
C
|
1-bromo-2-propanol |
D
|
2-propanol |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Separation and Purification | |
|
| 68 |
Go |
Q:
|
90 g of fructose (C6H12O6) is dissolved in 350 mL of water at 45 degrees Celcius. What is the approximate molality of this solution? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 69 |
Go |
Q:
|
Lead chloride dissolves in aqueous solution in the following fashion: PbCl2(s) → Pb2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq). An experiment is performed by adding 100 g of solid lead chloride to 500 mL of water; 85 g of lead chloride are found to be undissolved at the end of the experiment. Which of the following is the solubility product for the reaction? Assume the molar weight of lead chloride is 300 g. |
|
A
|
0.004 |
B
|
0.04 |
C
|
0.24 |
D
|
0.001 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 70 |
Go |
Q:
|
A solution is is made with a solvent and a particular molarity of solute. A solute with a higher Van 't Hoff factor will have: |
|
A
|
a lower boiling point. |
B
|
an elevated freezing point. |
C
|
a lower vapor pressure. |
D
|
a decreased number of electrolytes in solution. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 72 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the molality of a solution which contains 1 mole of sodium dissolved in 2 L of water? |
|
A
|
0.0005 m |
B
|
0.5 m |
C
|
2 m |
D
|
20 m |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 73 |
Go |
Q:
|
Sodium hypochlorite, NaClO, is highly soluble in water and decomposes to liberate O2(g). What would happen to the freezing point of a 0.05 M solution of sodium hypochlorite after it has completely decomposed? |
|
A
|
The freezing point would increase because the molarity of the solution would decrease. |
B
|
The freezing point would remain the same because the molarity of the solution would be unchanged. |
C
|
The freezing point would decrease because the molarity of the solution would increase. |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined from the given information. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | Solutions | |
|
| 74 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is FALSE regarding nonvolatile solutions? |
|
A
|
Nonvolatile solutions contain a solute with zero vapor pressure.
|
B
|
An example of a nonvolatile solution is a solution of salt in water.
|
C
|
Upon adding a nonvolatile solute to a liquid, the nonvolatile solution at the surface increases vapor pressure.
|
D
|
For a solution containing a nonvolatile solute, the vapor pressure is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure solvent multiplied by its mole fraction.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 75 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is true regarding the solubility of a gas? |
|
A
|
As temperature increases, the solubility of a gas increases.
|
B
|
As temperature decreases, the solubility of a gas decreases.
|
C
|
As pressure increases, the solubility of a gas decreases.
|
D
|
As pressure decreases, the solubility of a gas decreases.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Gases | |
|
| 76 |
Go |
Q:
|
Carbonation of an aqueous solution can be increased by: |
|
A
|
decreasing the pressure on the solution. |
B
|
decreasing the temperature of the solution. |
C
|
adding carbonic anhydrase. |
D
|
decreasing the surface area of the solution. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Gases | |
|
| 77 |
Go |
Q:
|
Glutamic acid is only very slightly soluble in water. Its solubility can be best increased by: |
|
A
|
adding NaCl to the solution. |
B
|
decreasing the temperature of the solution. |
C
|
adding acid to the solution |
D
|
increasing the pH of the solution. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Acid/Base Equilibria | |
|
| 78 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following would lower the freezing point of water the most? |
|
A
|
0.15 mM NaF |
B
|
0.1 mM FeCl3 |
C
|
0.2 mM glucose |
D
|
0.1 mM CaCl2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 79 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is true of a reversible reaction where Q > K? |
|
A
|
The reaction is at equilibrium. |
B
|
The reaction will increase the concentration of products over time. |
C
|
The reaction will increase the concentration of reactants over time. |
D
|
The reaction will be at equilibrium once the activation energy is reached. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 80 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the concentration sulfate in a 0.25 M solution of ferric sulfate Fe2(SO4)3? |
|
A
|
0.75 M |
B
|
0.25 M |
C
|
0.5 M |
D
|
3 M |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 81 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following would happen to hexanoic acid in an aqueous solution when the pH his changed from 3 to 6? |
|
A
|
Hexanoic acid would polymerize. |
B
|
Hexanoic acid would become more protonated. |
C
|
Hexanoic acid would become more soluble. |
D
|
Hexanoic acid would precipitate. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Carboxylic Acids | Acid/Base Equilibria | |
|
| 82 |
Go |
Q:
|
A 500mL solution of 4M KOH is diluted with 1.25 L of water. The final molarity of the solution is: |
|
A
|
0.75 M. |
B
|
1.15 M. |
C
|
1.85 M. |
D
|
2.3 M. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 83 |
Go |
Q:
|
To regulate osmotic balance, a cell loses 50 mM of sodium and gains 50 mM of potassium. Is the cell hypotonic, hypertonic, or isotonic to its surroundings? |
|
A
|
Hypotonic |
B
|
Isotonic |
C
|
Hypertonic |
D
|
Not enough information. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Membrane Transport and Signalling | Solutions | |
|
| 84 |
Go |
Q:
|
A solvent has a density 300g/L. 1 mole of a compound is dissolved in 1 L of the solvent. Which of the following is the approximate molality of the solution that is created? |
|
A
|
0.03 molal |
B
|
1 molal |
C
|
3 molal |
D
|
33 molal |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 85 |
Go |
Q:
|
One mole of CaCl2 is completely dissolved in 1L water. Which of the following is the resulting molarity of the solution? |
|
A
|
1 molar |
B
|
2 molar |
C
|
3 molar |
D
|
6 molar |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 86 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following salts would have the greatest freezing point depression capacity if 0.05 M were added to water? Assume total solubility of each. |
|
A
|
CaCl2 |
B
|
Al2(SO4)3 |
C
|
MgSO4 |
D
|
NaCl |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 87 |
Go |
Q:
|
250g of a solute are dissolved in 400cc of a solvent with a density of 0.6g/mL. Which of the following is the percent composition of mass of the solute in this solution? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 88 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds would be expected to have the highest boiling point? |
|
A
|
0.6m dextrose |
B
|
0.3m sodium chloride |
C
|
0.2m calcium chloride |
D
|
0.2m sodium phosphate |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 89 |
Go |
Q:
|
The solubility of calcium hydroxide is found to be 2 x 10-3 M. What is the Ksp for this reaction? |
|
A
|
3.2 x 10-8 |
B
|
1.6 x 10-8 |
C
|
1.6 x 10-6 |
D
|
3.2 x 10-5 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 90 |
Go |
Q:
|
A compound dissolves in the following reaction: X2Y3 → 2X+ + 3Y-. If the concentration of X is 0.2 M and the concentration of Y is 0.3 M, what is the approximate Ksp of the compound? |
|
A
|
0.01 M3 |
B
|
0.001 M3 |
C
|
0.002 M3 |
D
|
0.005 M3 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 91 |
Go |
Q:
|
16g of an unknown, nondissociating substance is dissolved in 1kg of benzene. This solution is noted to boil at 75 degrees celsius, whereas pure benzene boils at 73 degrees Celsius. The ebullioscopic constant, Kb, is 2.5 degreesC*kg/mol. What is the molecular weight of the unknown substance? |
|
A
|
15 g/mol |
B
|
20 g/mol |
C
|
25 g/mol |
D
|
30 g/mol |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 92 |
Go |
Q:
|
A solution is made with an unknown solute in 5L of water. This solution is found to have a molality of 15 molal. What is the molar mass of the compound if 300g of the solute are dissolved in the solution? |
|
A
|
1 g/mol |
B
|
4 g/mol |
C
|
26 g/mol |
D
|
40 g/mol |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 93 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the properties are not examples of colligative properties for solutions? |
|
A
|
osmotic pressure |
B
|
freezing point depression |
C
|
boiling point elevation |
D
|
reactivity of the solution |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 94 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is not a colligative property? |
|
A
|
Boiling point elevation |
B
|
Freezing point depression |
C
|
Density |
D
|
Vapor pressure |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 95 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is true regarding vapor pressure? |
|
A
|
when vapor pressure equals atmospheric pressure the solution boils |
B
|
lower vapor pressure implies lower boiling point |
C
|
intermolecular forces between molecules are strong for liquids with high vapor pressures |
D
|
increased vapor pressure implies a more dense liquid |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 96 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following substances is most soluble in water? |
|
A
|
AB, Ksp = 10-52 |
B
|
AB2, Ksp = 10-54 |
C
|
AB3, Ksp = 10-58 |
D
|
AB4, Ksp = 10-62 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 97 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following are examples of colligative properties?
I. freezing point depression
II. osmotic pressure
III. boiling point elevation |
|
A
|
III only |
B
|
I and III only |
C
|
I only |
D
|
I, II and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
| 98 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is the correct ordering of solubility of the following compounds in pentane?
I. phenol
II. 1,2-benzenediol
III. methylbenzene |
|
A
|
I > II > III |
B
|
III > I > II |
C
|
II > I > III |
D
|
IiI > II > I |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | |
|
|
Questions? We're here to help!
Ask Us
|