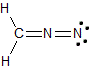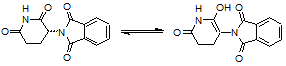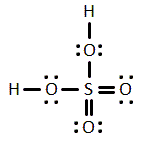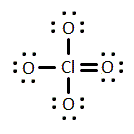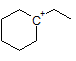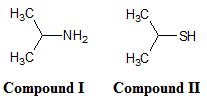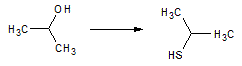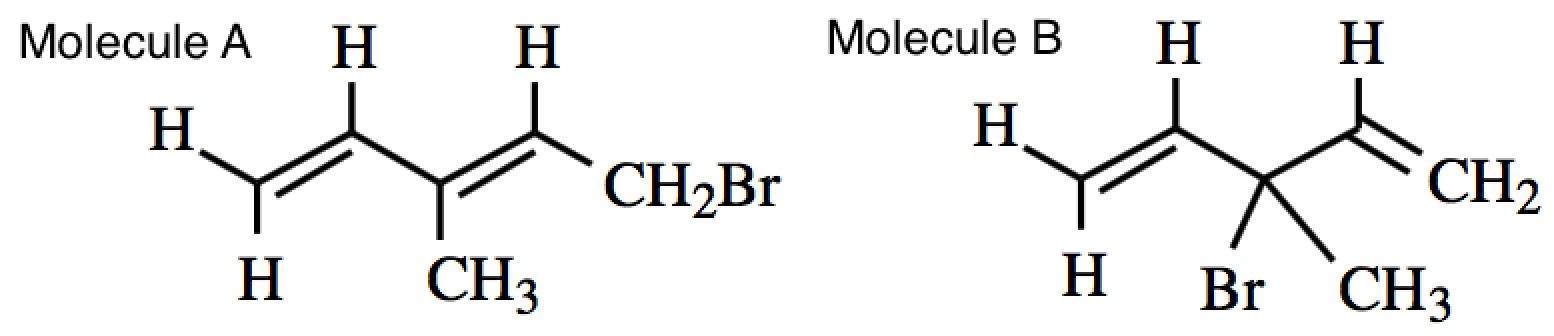|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
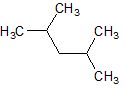
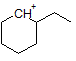
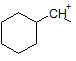
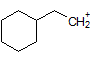
How many hydrogen peaks (excluding bond-neighbor effects) would the molecule 3-ethyl-2-methylpentane show in its H-NMR? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following cycloalkanes would be predicted to have the lowest reactivity? |
|
A
|
Cyclopropane |
B
|
Cyclohexane |
C
|
Cyclopentane |
D
|
Cyclobutane |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
How many H-NMR peaks would an individual expect to see in chlorobenzene? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is NOT characteristic of alkanes? |
|
A
|
Low reactivity |
B
|
Composed exclusively of hydrogen and carbon atoms in a formula proportional to CnH2n+2 |
C
|
Occur naturally in the environment |
D
|
Characterized by a high number of pi bonds |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
How many hydrogen peaks (excluding bond-neighbor effects) would the molecule 3-ethyl-2-methylpentane show in its H-NMR? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
Catalytic syn-addition hydrogenation by a poisoned catalyst of an alkyne produces what?
|
|
A
|
cis alkane |
B
|
trans alkene |
C
|
trans alkane |
D
|
cis alkene |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is most reactive with HCl? |
|
A
|
trans but-2-ene |
B
|
prop-1-ene |
C
|
cis but-2-ene |
D
|
but-1-ene |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following has an overall molecular dipole moment? |
|
A
|
benzene |
B
|
carbon dioxide |
C
|
methyl chloride |
D
|
acetylene |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following reactions necessarily inverts the stereochemistry of the compound?
I. SN1 reaction
II. SN2 reaction
III. E2 elimination |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
II only |
C
|
I and II |
D
|
I and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
You are told that a chloride containing compound has a molecular mass of 78.5 g/mol. Its H-NMR shows two signals, one which is split into 7 peaks and the other into 2 peaks. What is the compound? |
|
A
|
1-chloropropane |
B
|
1-chlorobutene |
C
|
2-chloropropane |
D
|
2-chloropropene |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
How many signals for 13C-NMR would we expect for bromobenzene? |
|
A
|
1 signal |
B
|
2 signals |
C
|
3 signals |
D
|
4 signals |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
The fingerprint region on an IR spectrum is the vibrational range in which specific functional groups within a molecule can be identified. A large, broad signal from 2900-3500 cm-1 accompanied by a strong, sharp peak at around 1700 cm-1 is usually indicative of what functional group? |
|
A
|
aldehyde |
B
|
amine |
C
|
carboxylic acid |
D
|
alcohol |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is not a criteria or not a true statement for aromaticity? |
|
A
|
All contributing atoms to the aromatic structure are on the same plane. |
B
|
The number of delocalized p-orbital electrons follows the rule 2n + 4, where n = 1, 2, 3, etc. |
C
|
Pyridine (C5H5N) is an aromatic molecule. |
D
|
Toluene (C6H5CH3) is an aromatic molecule.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
How many signals would we expect in C13-NMR for benzoic acid (benzene with a carboxyl group attached)? |
|
A
|
3 signals |
B
|
4 signals |
C
|
5 signals |
D
|
6 signals |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
Comparing cis-1,2-dibromoethene to trans-1,2-dibromoethene, which of the following is true? |
|
A
|
trans-1,2-dibromoethene has a dipole moment while cis-1,2-dibromoethene does not |
B
|
trans-1,2-dibromoethene experiences more steric hindrance than cis-1,2-dibromoethene |
C
|
cis-1,2-dibromoethene has a higher boiling point than trans-1,2-dibromoethene |
D
|
both compounds have identical physical and chemical properties |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
Replacing a methyl group on a 3° carbon with a phenyl group would most likely have which of the following effects? |
|
A
|
Increase the likelihood of a reaction via the SN1 mechanism rather than the SN2 mechanism. |
B
|
Decrease the boiling point of the molecule. |
C
|
Increase the solubility of the molecule in water. |
D
|
Decrease the toxicity of the molecule to mice. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
In the conversion of a ketone to a hemiketal, which of the following changes in the infrared spectrum would indicate completion of the reaction? |
|
A
|
Loss of a strong, sharp peak at 1700 cm-1 and appearance of broad peak around 3200 cm-1 |
B
|
Gain of a strong, sharp peak at 3200 cm-1 and loss of multiple smaller peaks at 2600, 1700, and 1400 cm-1 |
C
|
Gain of a strong, sharp peak at 2200 cm-1 and loss of a strong, sharp peak at 1700 cm-1 |
D
|
A change in the signature of the fingerprint region only |
|
|
|
Tags:
Aldehydes and Ketones | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds would be expected to have the highest λmax (wavelength of maximum absorption)? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following molecules does not have a permanent dipole?
|
|
A
|
NH3 |
B
|
CH2Cl2 |
C
|
H2O |
D
|
BH3 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 23 |
Go |
Q:
|
An unknown molecule is discovered to have exactly two chiral centers. Is the molecule necessarily chiral? |
|
A
|
Yes, because it has at least one chiral center. |
B
|
Yes, because as long as it has chiral centers, it is not superimposible on its mirror image. |
C
|
No, because molecules with an even number of chiral centers cannot be chiral. |
D
|
No, because it is still possible for molecules with multiple chiral centers to be sueprimposible on their mirror images. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 24 |
Go |
Q:
|
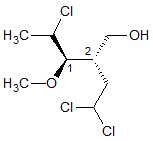
What is the absolute configuration of the carbon atoms labeled 1 and 2, respectively? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 25 |
Go |
Q:
|
Increased steric hindrance enhances the rate of SN1 reactions versus SN2 reactions because |
|
A
|
it is more difficult for the nucleophile to attack a sterically-hindered molecule. |
B
|
steric hindrance increases reactivity which makes SN1 reactions more likely. |
C
|
steric hindrance protects the nucleophile from reacting with the solvent. |
D
|
nucleophilic attack of sterically-hindered molecules is easier than non-sterically-hindered molecules. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Organic Chemistry Reactions | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 26 |
Go |
Q:
|
The molecule sulfur hexafluoride, SF6 is nonpolar because |
|
A
|
there is no dipole formed between sulfur and fluorine |
B
|
octahedral molecules cannot be polar |
C
|
sulfur-containing compounds cannot be polar |
D
|
the bonds in the molecule are arranged such that the vectors of each bond dipole cancel out |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 27 |
Go |
Q:
|
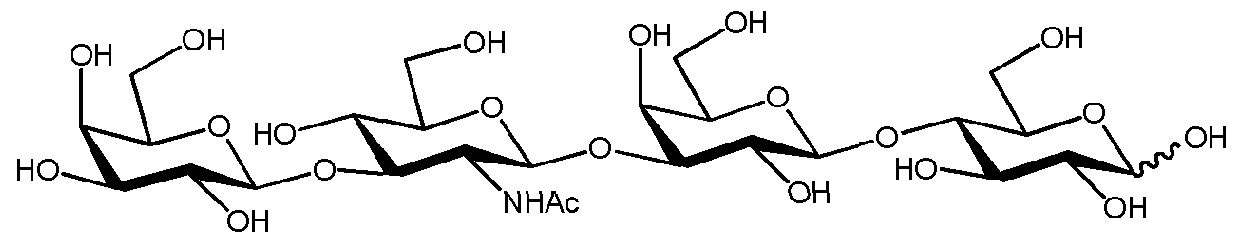
Polyglycine is a polypeptide composed of a string of glycine residues. It is a model polypeptide for many of its properties since glycine is the simplest amino acid. Compared to polyarginine composed of 20 residues, one can expect polyglycine composed of 20 residues to |
|
A
|
have a wider range of torsional angles due to decreased steric hindrance |
B
|
have a higher effective pKa |
C
|
form a more basic solution |
D
|
have a higher molecular weight |
|
|
|
Tags:
Protein Structure and Function | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 28 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is true regarding meso compounds?
I. They are optically inactive
II. They must have two stereogenic centers
III. They are achiral molecules |
|
A
|
I and and II only |
B
|
I and III only |
C
|
II and III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 29 |
Go |
Q:
|
Mass spectrometry is an analytic tool used to identify molecular fragments and piece together the original compound based on the identity of those fragments. Which of the following accurately indicates the factors used to identify the molecular fragments?
I. mass
II. charge
III. molar absorptivity |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
I and II only |
C
|
III only |
D
|
I and III only |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 30 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular molecule is found to have 3 stereocenters. Excluding that molecule, how many diastereomers exist? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 31 |
Go |
Q:
|
The reaction below shows the conversion of racemic thalidomide in its keto form into its enol form. The relationship between the two molecules is known as which of the following?
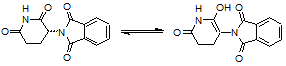 |
|
A
|
enantiomerism |
B
|
diastereomerism |
C
|
tautomerism |
D
|
conformational isomerism |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 32 |
Go |
Q:
|
At immense pressures, hydrogen undergoes a phase transition to a unique state. In this state, the space between hydrogen atoms is less than their Bohr radius, meaning electron clouds overlap significantly. This overlap explains which of the following phenomena of this state of hydrogen? |
|
A
|
its lack of a triple point with any other state of hydrogen |
B
|
its density being lower than at STP |
C
|
its ability to conduct electricity |
D
|
its lack of color |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 33 |
Go |
Q:
|
Most chiral nitrogens are unstable and readily interconvert their stereochemistry spontaneously to form racemic mixtures. This process can be slowed to maintain the stereochemistry of the nitrogen atoms in which of the following ways? |
|
A
|
increasing the pH of the solution |
B
|
decreasing the size of functional groups on the nitrogen |
C
|
increasing the temperature of the solution |
D
|
increasing the steric hindrance of the functional groups on the nitrogen |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 34 |
Go |
Q:
|
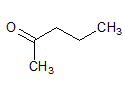
How many proton NMR signals would be expected for 3-pentanone, neglecting peak splitting? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 35 |
Go |
Q:
|
The following is a molecule of alpha-D-glucopyranose. How many epimers does the following molecule have?
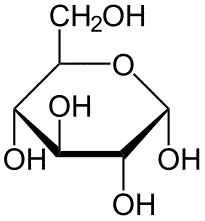
|
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 36 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following conditions decreases the nucleophilicity of a compound? |
|
A
|
decrease in steric hindrance |
B
|
decrease in electron density |
C
|
increase in its strength as a base |
D
|
increase in its electron-density donating groups |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 37 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following molecules is amphoteric in a solution? |
|
A
|
Table salt |
B
|
Borane (BH3) |
C
|
Hydrobromic acid |
D
|
Glycine |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 39 |
Go |
Q:
|

What is the absolute configuration of carbon atoms 1 and 2, respectively, in the compound above? |
|
A
|
R, R |
B
|
R, S |
C
|
S, R |
D
|
S, S |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 40 |
Go |
Q:
|
How many discrete 1H-NMR signals would be expected to be seen in 2-propanol? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 41 |
Go |
Q:
|
In which of the following conditions will plane-polarized light NOT be rotated?
I. an achiral compound
II. a meso compound
III. a racemic mixture |
|
A
|
I and II only |
B
|
III only |
C
|
I and III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 42 |
Go |
Q:
|
Certain functional groups will absorb at multiple different wavelengths in infrared spectroscopy. This absorbance at multiple wavelengths is due to |
|
A
|
different types of bond motions including vibrations and stretches. |
B
|
intramolecular interactions of other functional groups. |
C
|
resonant absorbance frequencies. |
D
|
conjugation in the molecule. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 44 |
Go |
Q:
|
Melamine, a heterocyclic compound with the chemical formula C3H6N6 can be added to foods to artificially increase their protein content in certain analytical methods. These analytical methods most likely detect protein content as a measure of |
|
A
|
the quantity of carbon present in the sample. |
B
|
the quantity of nitrogen present in the sample. |
C
|
the ratio of carbon to oxygen in the sample. |
D
|
the quantity of sulfur in the sample. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 45 |
Go |
Q:
|
The 1H NMR of a compound yields two distinct peaks: one doublet and one quartet. It molecular formula is found to be C4H8. After a reaction, the 1H NMR of the product yields one singlet peak. The product still contains 4 carbon atoms. Which of the following types of reactions occurred? |
|
A
|
hydration |
B
|
halogenation with HCl |
C
|
dehydrogenation |
D
|
nucleophilic substitution
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 46 |
Go |
Q:
|
In mass spectrometry, two ions will be depicted as a single peak if which of the following is true? |
|
A
|
One ion has a mass of M and a charge of Z and the other ion has a mass of 2M and a charge of 2Z |
B
|
One ion has a mass of M and a charge of Z and the other ion has a mass of 2M and a charge of Z/2 |
C
|
One ion has a mass of M and a charge of Z and the other ion has a mass of M/2 and a charge of Z |
D
|
Two ions will occupy the same peak so long as they are fragments of the same original molecule. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 47 |
Go |
Q:
|
A molecule with square planar geometry, like XeF4 has different geometry from SiCl4 because: |
|
A
|
Xe is an inert gas. |
B
|
Fluorine is more electronegative than Xenon. |
C
|
The bond angles for the square planar geometry are larger than for the tetrahedral geometry, making XeF4 more stable as a square planar molecule. |
D
|
XeF4 has two lone pairs in addition to the four bonds. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 48 |
Go |
Q:
|
The molecular geometry of NH3 is LEAST like which of the following? |
|
A
|
BH3 |
B
|
CH4 |
C
|
SH2 |
D
|
SO42- |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 49 |
Go |
Q:
|
A carbanion can be stabilized in which of the following ways? |
|
A
|
The addition of halogen atoms to the carbanion's substituent groups. |
B
|
Increasing its solution temperature. |
C
|
The addition of aliphatic groups to the carbanion's substituent groups. |
D
|
Its placement in a nonpolar solvent. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 50 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds is NOT planar? |
|
A
|
BF3 |
B
|
NH3 |
C
|
C2H4 |
D
|
XeF4 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 52 |
Go |
Q:
|
Biuret reagent is a solution which reacts with proteins to reduce Cu2+ to Cu+ which allows for quantitative detection at 540 nm. The best method for quantifying the protein would be: |
|
A
|
Infrared Spectroscopy |
B
|
H1 NMR |
C
|
Mass Spectrometry |
D
|
UV-Visible Spectroscopy |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 54 |
Go |
Q:
|
HCl has a lower boiling point than HI. The reason for this can be best attributed to which of the following? |
|
A
|
HCl is more polar than HI |
B
|
HCl is less polar than HI |
C
|
HCl is much larger than HI |
D
|
HCl is much smaller than HI |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 55 |
Go |
Q:
|
A brand of rock salt is rated down to -25 °C. The salt is indicated to be mostly composed of NaCl. Exposed to temperatures of -35 °C the salt ceases to work. If the NaCl rock salt were replaced with CaCl2 with the same molality, would the ice melt? |
|
A
|
No, because the salts are placed in the same molality. |
B
|
No, because the additional melting power of the CaCl2 would be insufficient to melt ice at -35 °C. |
C
|
Yes, because the CaCl2 would be able to melt ice down to -37.5 °C. |
D
|
Yes, because melting of CaCl2 is exothermic. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | Thermochemistry | |
|
| 56 |
Go |
Q:
|
The IR spectra of carboxylic acids and aldehydes should share a strong, sharp peak near a frequency of: |
|
A
|
1700 cm-1. |
B
|
3300 cm-1. |
C
|
2200 cm-1. |
D
|
1100 cm-1. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 57 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following would be expected of the product of the reaction between acetic acid and SOCl2? |
|
A
|
The product will boil at a lower temperature than acetic acid. |
B
|
The product will form hydrogen bonds. |
C
|
The product will lose its carbonyl. |
D
|
The product and acetic acid will be inseparable using distillation. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Alcohols | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 58 |
Go |
Q:
|
Beta-D-glucose has 5 stereocenters with the designations: 1S, 2R, 3S, 4S, 5R. Which of the following stereocenter designations below is the enantiomer of Beta-D-glucose? |
|
A
|
1R, 2S, 3R, 4R, 5S |
B
|
1S, 2S, 3S, 4R, 5R |
C
|
1R, 2S, 3S, 4R, 5R |
D
|
1R, 2S, 3R, 4S, 5S |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 59 |
Go |
Q:
|
The oxidation of hexanol to hexanoic acid would be accompanied by the appearance of which of the following peaks in an IR spectrum? |
|
A
|
1400 cm-1 |
B
|
1650 cm-1 |
C
|
2300 cm-1 |
D
|
3300 cm-1 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 60 |
Go |
Q:
|
The transformation of 2-methylbutene to 2-ethylbutane requires a transformation from |
|
A
|
An sp orbital to an sp3 orbital |
B
|
An sp3 orbital to an sp2 orbital |
C
|
An sp2 orbital to an sp3 orbital |
D
|
An sp3 orbital to an sp orbital |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 61 |
Go |
Q:
|
(CH3CH2)3N is a weak nucleophile primarily because it is |
|
A
|
weakly basic |
B
|
sterically hindered |
C
|
electron-dense |
D
|
alkylated |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 62 |
Go |
Q:
|
A new drug is developed and a pill, Pill X, is made up of 25% S-(+)-configuration and 75% R-(-)-configuration. It is found that the S configuration is actually the active form of the drug, therefore a new pill, Pill Y, is developed which contains 100% S-configuration. Which of the following holds true regarding these pills? |
|
A
|
Pill X rotates light clockwise. |
B
|
Pill Y rotates light more clockwise than Pill X. |
C
|
Pill X and Pill Y will rotate light the same number of degrees, but in difference clockwise/counter-clockwise directions. |
D
|
Pill Y rotates light counterclockwise. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 63 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following holds true regarding conformational isomers? |
|
A
|
They contain less similarity than stereoisomers |
B
|
Eclipsed conformation is always less favorable than staggered |
C
|
They all exist at the same energy state |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 64 |
Go |
Q:
|
A carbocation is surrounded by two hydrogen atoms and a third group. Which of the following third groups bound to the carbocation would render the carbocation most stable? |
|
A
|
methyl group |
B
|
nitro group |
C
|
fluoride group |
D
|
carboxyl group |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 66 |
Go |
Q:
|
α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-glucopyranose are:
I. Anomers
II. Epimers
III. Diastereomers |
|
A
|
III only |
B
|
I and III only |
C
|
I and II only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 67 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds will have three distinct signals on a 1H-NMR spectrum? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 68 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds would be expected to have the least amount of steric strain on its bonds? |
|
A
|
cyclopropane |
B
|
cyclobutane |
C
|
cyclopentane |
D
|
cyclohexane |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 69 |
Go |
Q:
|
while monitoring a reaction, a student gathers the IR spectra at different timepoints. A strong, broad peak at 3200 cm-1 is slowly replaced with a strong, sharp peak at 1750 cm-1 upon completion of the reaction. Which of the following conversions has most likely occurred? |
|
A
|
C-C to C=C |
B
|
C=O to C-OH |
C
|
C-OH to C=O |
D
|
C=O to C=N |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 70 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is LEAST likely to impact the boiling point of a solvent? |
|
A
|
The number of hydrogen bonds it can form |
B
|
The molecular weight of the molecule |
C
|
The presence of d-orbitals in any of its atoms |
D
|
The presence of charged species on the atom |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 71 |
Go |
Q:
|
SN2 reactions involve inversion of the nucleophile and leaving group sites. This is primarily due to: |
|
A
|
steric hindrance from the leaving group. |
B
|
the strength of the nucleophile in SN2 reactions. |
C
|
the stability of the leaving group in solution. |
D
|
the polarity of the reaction solvent. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 72 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following molecules is least polar? |
|
A
|
SH2 |
B
|
H2O |
C
|
CO2 |
D
|
CCl2H2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 73 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding primary and secondary amines? |
|
A
|
Primary amines are in general stronger bases than secondary amines. |
B
|
Primary amines are less sterically hindered than secondary amines. |
C
|
Primary and secondary amines both have a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. |
D
|
Primary and secondary amines can both be used in the production of an amide. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | Acid/Base Equilibria | |
|
| 75 |
Go |
Q:
|
A compound is found to have a strong, sharp peak around 1690 cm- in its IR spectrum. Which of the following candidates could it NOT be? |
|
A
|
formic acid |
B
|
methylamine |
C
|
ethyl propanoate |
D
|
benzaldehyde |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 76 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the compounds shown below is more soluble in water?
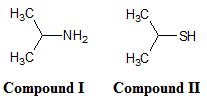 |
|
A
|
Compound I |
B
|
Compound II |
C
|
They are approximately equally soluble |
D
|
Neither has appreciable water solubility |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 77 |
Go |
Q:
|
TLC is performed on samples at different time points of a reaction. The matrix is a polar stationary phase and the mobile phase used is a 1:10 ratio of ethyl acetate:diethyl ether. Blots in early time points show a compound with an Rf value of 0.38 slowly diminishing and being replaced with a compound with an Rf value of 0.22. Which of the following reactions could have taken place? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 78 |
Go |
Q:
|
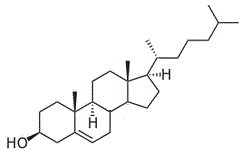
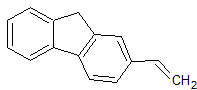
The diagram above shows the structure of cholesterol. How many stereocenters does the molecule have? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 79 |
Go |
Q:
|
How many different constitutional isomers can be formed using the formula C5H12? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 80 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following describes the transition in molecular geometry as PF5 loses a fluorine atom to become PF4-. |
|
A
|
Trigonal bi-pyramidal to see-saw |
B
|
Trigonal bi-pyramidal to square planar |
C
|
Trigonal bi-pyramidal to tetrahedral |
D
|
Octahedral to trigonal bi-pyramidal |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 81 |
Go |
Q:
|
The emission spectrum of hydrogen in the visible region includes lines at 410 nm, 434 nm, 486 nm, and 656 nm. Given that hydrogen only has a single electron, which of the following best explains its ability to have multiple emission lines? |
|
A
|
Each emission line corresponds to the electron dropping from different energy levels after excitation. |
B
|
Hydrogen electrons are delocalized during excitation and each atom can temporarily acquire multiple electrons for excitation. |
C
|
The single electron emits all of the lines simultaneously as it drops its energy level. |
D
|
The energy of the lines must be combined to yield the true energy of the electron. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 82 |
Go |
Q:
|
Morphine, a chiral compound, is illustrated below. How many sterogenic carbon centers are there in morphine?
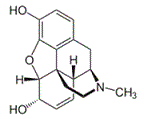
|
|
A
|
5 |
B
|
6 |
C
|
7 |
D
|
More than 7 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 84 |
Go |
Q:
|
Ibuprofen has both an (R) and an (S) set of enantiomers, with the (S) form being the pharmacologically active form of the drug. In studies, scientists attempted to optimize the effectiveness of the drug by administering only the (S) form, but found no significant improvements in drug efficiency. Which of the following best explains the findings? |
|
A
|
The (R) enantiomer is pharmacologically active through another pathway. |
B
|
There is a maximum amount of (S) enantiomer that can be administered at any given time before the addition of more drug ceases to have an effect. |
C
|
An enzyme exists which catalyzes the conversion of the (R) to the (S) isomer in vivo. |
D
|
The enantiomers do not racemize when in solution. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 85 |
Go |
Q:
|
I2 has a much higher boiling point than Cl2 because: |
|
A
|
Cl2 is more polar than I2. |
B
|
Cl2 is larger than I2. |
C
|
I2 is more polar than Cl2. |
D
|
I2 is larger than Cl2. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 86 |
Go |
Q:
|
Acetaldehyde, CH3CHO is considered prochiral because it can be converted into a chiral compound in a single step. Which of the following would cause acetaldehyde to form a chiral product? |
|
A
|
Addition of an -OH group |
B
|
Addition of an -H group |
C
|
Replacement of the C=O group with 2 -H groups |
D
|
Addition of an -OCH3 group |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 87 |
Go |
Q:
|
The 1H-NMR spectrum of an organic molecule returns as a single peak. Which of the following could NOT be the molecule in question? |
|
A
|
methane |
B
|
ethane |
C
|
propadiene |
D
|
2-methylpropane |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 88 |
Go |
Q:
|
The following molecule is called cortisone, a steroid hormone. How many stereoisomers (excluding cortisone) exist for this molecule?
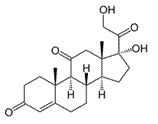 |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 90 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is true regarding a molecule with sp3 hybridized orbitals? |
|
A
|
Its structure is always tetrahedral |
B
|
Its structure is always trigonal planar |
C
|
The angles between the groups will consistently be 109.5 degrees |
D
|
Its structure is determined by the groups bound to the central atom |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 92 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following reactions, if it takes place at an (R) stereocenter, will produce a racemic mixture with respect to that stereocenter? |
|
A
|
SN1 |
B
|
SN2 |
C
|
E1 |
D
|
(A) and (B) |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 93 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is true for meso compounds? |
|
A
|
They necessarily have 2 or more stereocenters |
B
|
They have at least two (R) or at least two (S) stereocenters. |
C
|
They may have optical activity, however most are optically inactive |
D
|
They have exactly one enantiomer |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 94 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular molecule exists in both an (R) and (S) configuration. A mixture of these two is found to rotate light +30 degrees. It can be assumed that |
|
A
|
the number of (R) molecules is greater than the number of (S) molecules |
B
|
the number of (S) molecules is greater than the number of (R) molecules |
C
|
the number of (S) molecules is greater than the number of (R) molcules OR the number of (R) molecules is greater than the number of (S) molecules |
D
|
we are unable to discern the relationships between the number of (R) and (S) molecules |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 95 |
Go |
Q:
|
A molecule with 0 chiral centers can only have which of the following? |
|
A
|
a diastereomer |
B
|
a conformational isomer |
C
|
an enantiomer |
D
|
an epimer |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 96 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is FALSE regarding isomers and chirality? |
|
A
|
Diastereomers cannot also be enantiomers |
B
|
A carbon with a double bond to another carbon atom could form TWO isomers |
C
|
Any amino acid is a chiral molecule |
D
|
Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images of each other |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 97 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the structure below, the hybridization, electronic geometry, and observable geometry of the oxygen atom is:
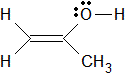
|
|
A
|
sp2, trigonal planar, trigonal planar |
B
|
sp2, trigonal planar, bent |
C
|
sp3, tetrahedral, tetrahedral |
D
|
sp3, tetrahedral, trigonal pyramidal |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 99 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the molecule below, which of the following best describes the dipole moment?
 |
|
A
|
Dipole moment present, points toward sulfur
|
B
|
Dipole moment present, points toward the chlorines
|
C
|
Dipole moment present, points toward the carbons
|
D
|
No dipole moment present
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 100 |
Go |
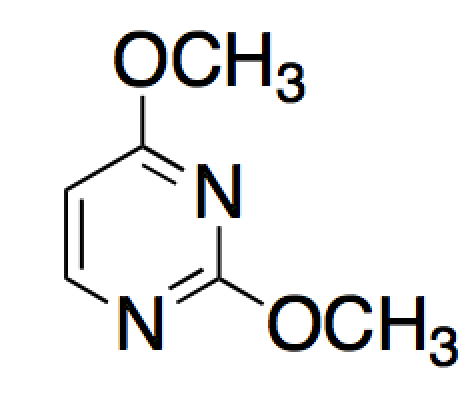
Q:
|
The molecule below has a pKa greater than 40. If a neutral nitrogen replaces the carbon at the fourth position on the ring, what will happen to the pKa and why?
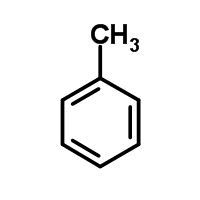 |
|
A
|
The pKa will increase because the introduction of the nitrogen atom eliminates any resonance
|
B
|
The pKa will increase because once the molecule is deprotonated, the negative charge can be stabilized by the more electronegative nitrogen atom
|
C
|
The pKa will decrease because the introduction of the nitrogen atom eliminates any resonance
|
D
|
The pKa will decrease because once the molecule is deprotonated, the negative charge can be stabilized by the more electronegative nitrogen atom
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Acid/Base Equilibria | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 101 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the molecule below, which of the following best describes its polarity, (if any)?
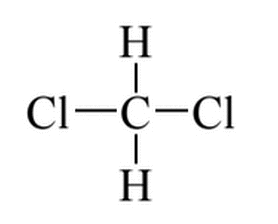 |
|
A
|
Polar with an overall molecular dipole moment
|
B
|
Nonpolar with an overall molecular dipole moment
|
C
|
Polar without an overall molecular dipole moment
|
D
|
Nonpolar without an overall molecular dipole moment
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 102 |
Go |
Q:
|
Hydroformylation involves the addition of a formaldehyde (formyl groupe) onto alkenes. For a hydroformylation process with propene that follows Markovnikov addition using a carbocation intermediate, which product will be favored? |
|
A
|
butanal |
B
|
2-methylpropanal |
C
|
2-methylbutanal |
D
|
propanal |
|
|
|
Tags:
Organic Chemistry Reactions | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 103 |
Go |
Q:
|
The reaction below depicts a 1,2-hydride shift which is a reaction that heavily favors the products.

The reason for strongly favoring the products is:
|
|
A
|
the primary cabocation is more charged than the secondary carbocation and pulls the hydrogen atom toward itself |
B
|
the hydride shift favors a secondary carbocation rather than a primary carbocation |
C
|
methyl groups are more electronegative and pull positive charges toward themselves |
D
|
the secondary carbocation is less stericaly hindered than the primary carbocation |
|
|
|
Tags:
Organic Chemistry Reactions | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 104 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following correctly describes a polar covalent bond? |
|
A
|
Involves a transfer of electrons to the atom of less electronegativity
|
B
|
Involves equal sharing of an electron pair between two atoms
|
C
|
Involves unequal sharing of an electron pair between two atoms
|
D
|
Results in the formation of oppositely charged ions
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 105 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the molecule below, and the choice between the nitrogen and oxygen atoms, where will protonation more likely occur and why?
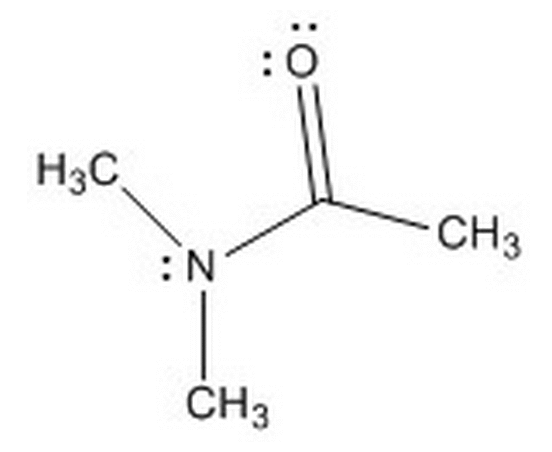 |
|
A
|
Oxygen because there are no delocalized electrons present, meaning it is a stronger base when protonated
|
B
|
Nitrogen because the delocalized electrons on the nitrogen make it more stable, and thus, a stronger base than the oxygen
|
C
|
Oxygen because the delocalized electrons on the nitrogen make it more stable, and thus, a weaker base than the oxygen
|
D
|
Nitrogen because it is more electronegative than oxygen, and once protonated, will have a lower pka than the protonated oxygen
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Acid/Base Equilibria | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 106 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the connectivity below, which of the following classifications/descriptions do NOT apply to the two isomers possible due to the carbon bonded to the bromine?
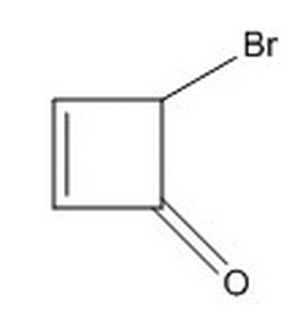 |
|
A
|
Enantiomers |
B
|
Diastereomers |
C
|
Stereoisomers |
D
|
Both molecules are optically active
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 107 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the molecule below, which of the following choices best describe its aromaticity and delocalized electrons?
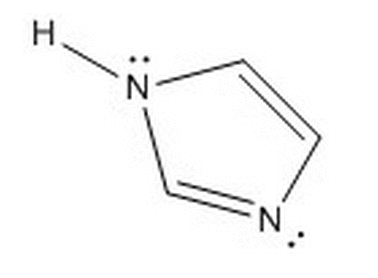 |
|
A
|
Aromatic, 4 delocalized electrons
|
B
|
Not aromatic, 2 delocalized electrons
|
C
|
Aromatic, 6 delocalized electrons
|
D
|
Not aromatic, 6 delocalized electrons
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 108 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following correctly ranks the bond lengths shown in the molecule below?
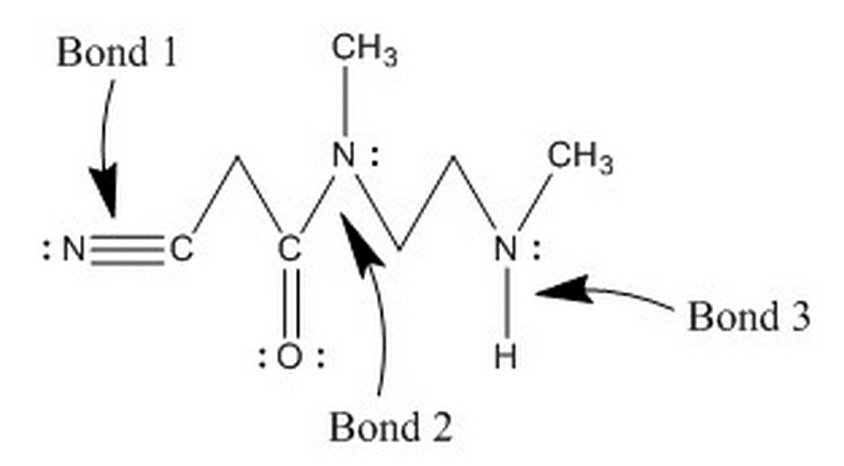 |
|
A
|
1 > 2 > 3
|
B
|
3 > 1 > 2
|
C
|
2 > 3 > 1
|
D
|
2 > 1 > 3
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 110 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the reaction below, how many atoms in the aromatic ring were oxidized and how many were reduced?
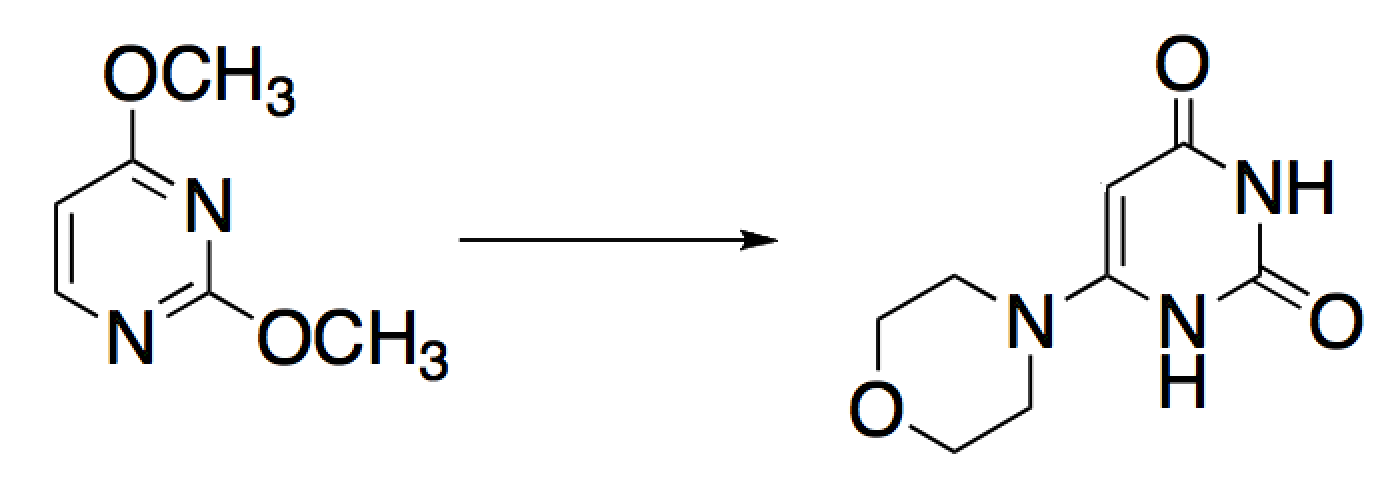
|
|
A
|
0 atoms oxidized, 1 atom reduced
|
B
|
1 atom oxidized, 0 atoms reduced
|
C
|
1 atom oxidized, 1 atom reduced
|
D
|
2 atoms oxidized, 1 atom reduced
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Redox Reactions | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 111 |
Go |
Q:
|
In each molecule below, a carbocation is formed when the alcohol group is removed. Which of the following best describes the stabilities of the carbocations?
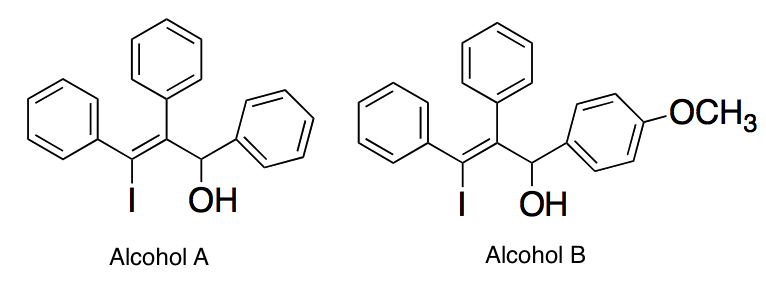
|
|
A
|
The carbocation of Alcohol A is more stable than the carbocation of Alcohol B since it lacks a methoxy group, which would destabilize the carbocation
|
B
|
The carbocation of Alcohol A is less stable than the carbocation of Alcohol B since it lacks a methoxy group, which would destabilize the carbocation
|
C
|
The carbocation of Alcohol B is more stable than the carbocation of Alcohol A since it has a methoxy group, which would stabilize the carbocation
|
D
|
The carbocation of Alcohol B is less stable than the carbocation of Alcohol A since it has a methoxy group, which would stabilize the carbocation
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | Organic Chemistry Reactions | |
|
| 112 |
Go |
Q:
|
What are the oxidation states of Atom A and Atom B in the molecule below?
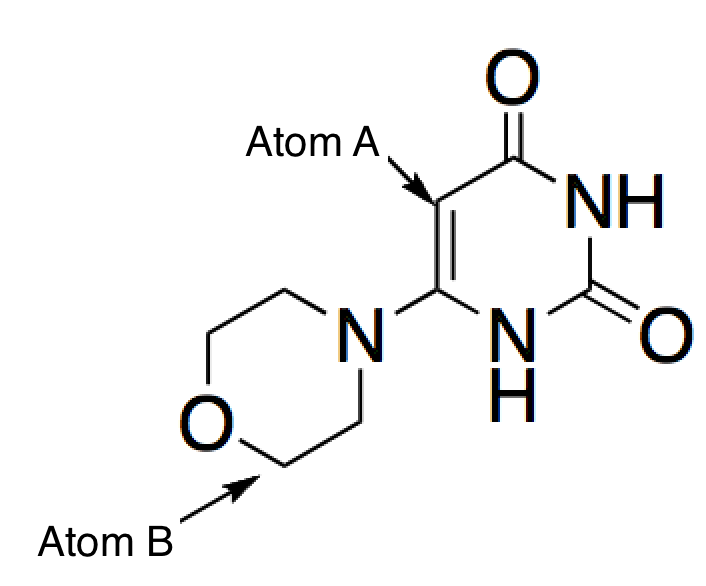
|
|
A
|
0, -1 |
B
|
-1, 0
|
C
|
-1, -1
|
D
|
0, 0
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 113 |
Go |
Q:
|
In each molecule below, a carbocation is formed when the alcohol group is removed. Which of the following best describes the stabilities of the carbocations?
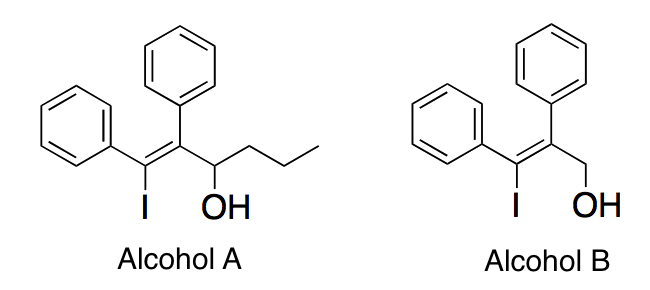 |
|
A
|
The carbocation of Alcohol A is more stable than the carbocation of Alcohol B since it is non-resonance stabilized
|
B
|
The carbocation of Alcohol A is less stable than the carbocation of Alcohol B since it is resonance de-stabilized
|
C
|
The carbocation of Alcohol B is more stable than the carbocation of Alcohol A since it is a resonance stabilized primary carbocation
|
D
|
The carbocation of Alcohol B is less stable than the carbocation of Alcohol A since it is a resonance stabilized primary carbocation
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | Alcohols | |
|
| 114 |
Go |
Q:
|
In the following reaction, the fastest reaction rate occurs in pure water, as opposed to occurring in a solvent like ethanol. Which of the following best describes why this scenario takes place?
 |
|
A
|
The aromatic rings in both reactants are hydrophobic and will be in close proximity to each other, which increases the chance of a reaction taking place
|
B
|
The aromatic rings in both reactants are hydrophobic and will be in close proximity to each other, which decreases the chance of a reaction taking place
|
C
|
The aromatic rings in both reactants are hydrophilic and will be in close proximity to each other, which increases the chance of a reaction taking place
|
D
|
The aromatic rings in both reactants are hydrophilic and will be in close proximity to each other, which decreases the chance of a reaction taking place
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Carboxylic Acids | Molecular Structure | Organic Chemistry Reactions | |
|
| 115 |
Go |
Q:
|
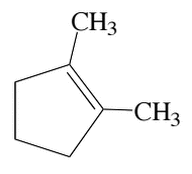
An allylic substitution reaction results in two regioisomeric monobromides, as shown below. Which of the following statements about their relative stabilities is correct?
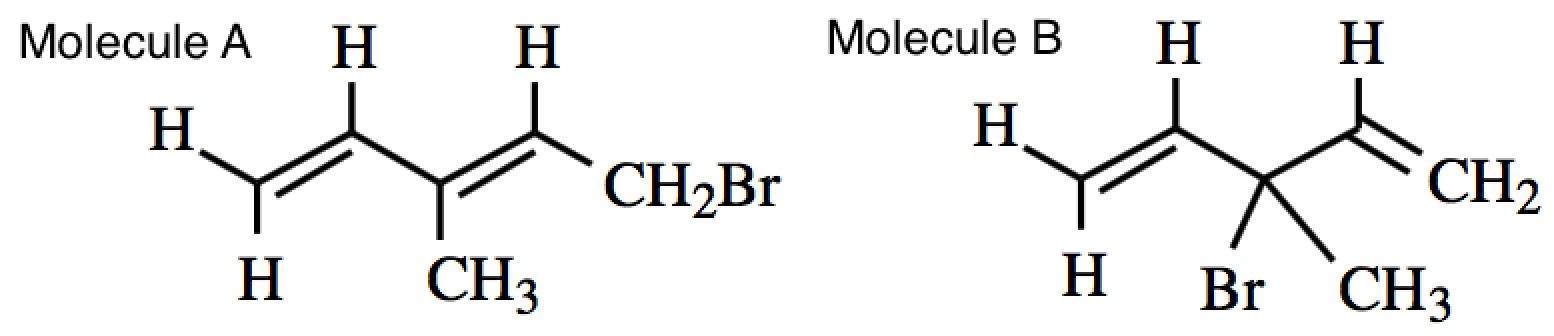 |
|
A
|
Molecule A is more stable because it has a more sterically hindered bromine.
|
B
|
Molecule A is more stable because it has conjugated double bonds.
|
C
|
Molecule B is more stable because it has a less sterically hindered bromine.
|
D
|
Molecule B is more stable because it has conjugated double bonds.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Molecular Structure | Organic Chemistry Reactions | |
|
| 116 |
Go |
Q:
|
The following molecule is an activated carboxylic acid derivative, which can be used as an acylating agent. Which of the following is TRUE regarding its nitrogen-based leaving group?
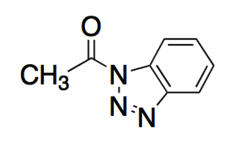 |
|
A
|
The nitrogen-based leaving group is a poor leaving group since there is more resonance stabilization in its current form.
|
B
|
The nitrogen-based leaving group is a poor leaving group since it is large and uncharged.
|
C
|
The nitrogen-based leaving group is a good leaving group since its negative charge (upon leaving) is stabilized by resonance.
|
D
|
The nitrogen-based leaving group is a good leaving group since it retains its neutral charge even after leaving the molecule.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | Acid Derivatives | |
|
| 118 |
Go |
Q:
|
The nitrogen-containing reactant below (Reactant B) can act as a nucleophile in certain reactions. The reaction below is carried out in a pH = 4.5 buffer. This is because the pKa of the protonated carbonyl (Reactant A) is between -2 and -8, so there is a low concentration of this highly reactive electrophile at a pH of 4.5. If the pH is further lowered (from 4.5) in order to try and increase the concentration of this electrophile, which of the following correctly describes the likely counter-effect?
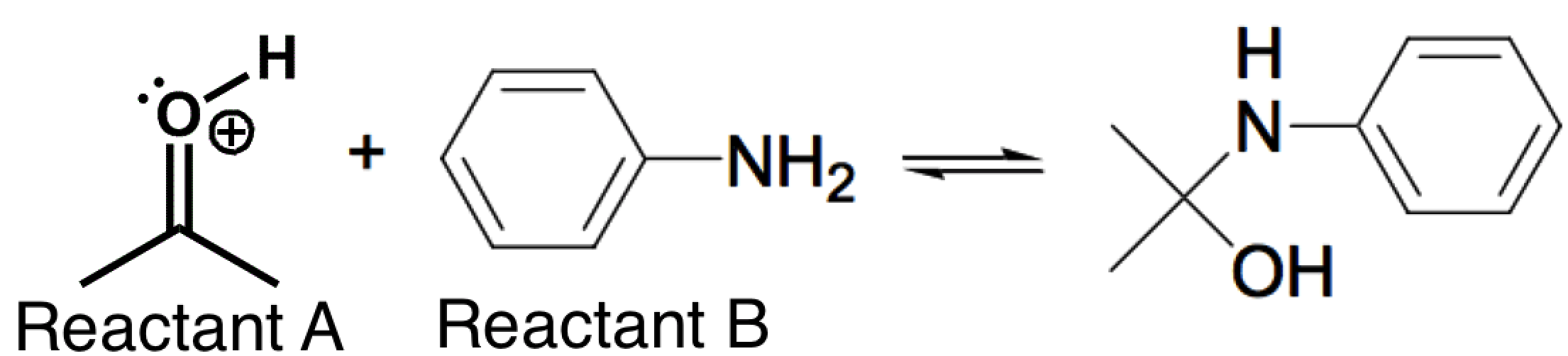 |
|
A
|
Increasing the acidity would cause less of Reactant B to become protonated (decreasing its nucleophilicity), and this would counteract the increase in electrophilicity of Reactant A.
|
B
|
Increasing the acidity would cause more of Reactant B to become protonated (decreasing its nucleophilicity), and this would counteract the increase in electrophilicity of Reactant A.
|
C
|
Increasing the acidity would cause more of Reactant B to become protonated and this would have no effect on the electrophilicity of Reactant A.
|
D
|
Increasing the acidity would have no effect on Reactant B and no effect on the electrophilicity of Reactant A.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Acid/Base Equilibria | Miscellaneous Organic Chemistry | Organic Chemistry Reactions | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 119 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the molecule below, which of the following is TRUE regarding its ability (or inability) to undergo an acylation reaction?
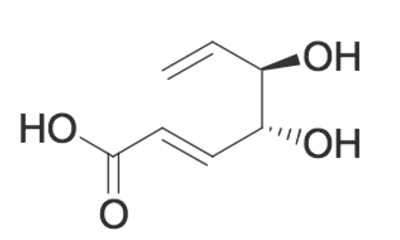 |
|
A
|
The molecule will undergo an intramolecular acylation reaction between the wedged alcohol and the carboxylic acid
|
B
|
The molecule will undergo an intramolecular acylation reaction between the dashed alcohol and the carboxylic acid
|
C
|
The molecule will NOT undergo an intramolecular acylation reaction because the double bond does not allow for the interaction between the alcohols and the carboxylic acid
|
D
|
The molecule will NOT undergo an intramolecular acylation reaction because acylation reactions cannot occur with carboxylic acids.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Carboxylic Acids | Organic Chemistry Reactions | Molecular Structure | Alcohols | |
|
| 120 |
Go |
Q:
|
Two different alcohols (R1 and R2) undergo a transesterification reaction using the same reactant, as shown below. Which of the following best explains the most likely product yields?
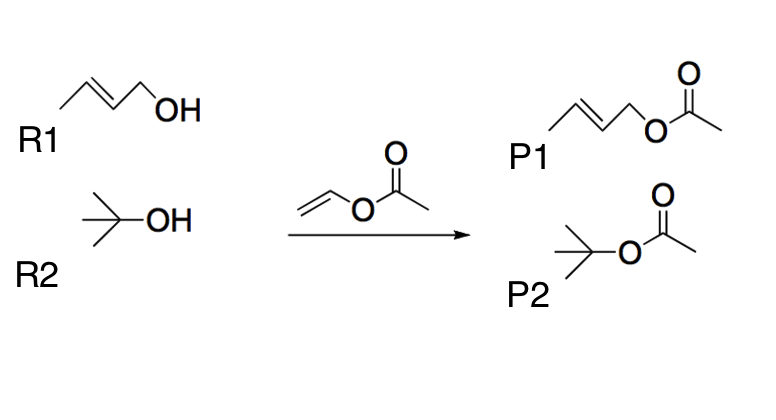 |
|
A
|
P1 will have the least yield because R1 is a primary alcohol and will not undergo a transesterification reaction.
|
B
|
P1 will have the most yield because R1 is a primary alcohol and is the least sterically hindered.
|
C
|
P2 will have the most yield because R2 is a tertiary alcohol and is the most sterically hindered.
|
D
|
P2 will have the most yield because R2 is the most basic alcohol.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Aldehydes and Ketones | Alcohols | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 121 |
Go |
Q:
|
SO42- is most similar in molecular geometry to: |
|
A
|
PCl5 |
B
|
H2O |
C
|
SCl2 |
D
|
CH4 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 122 |
Go |
Q:
|
The molecular geometry of BF3 is closest to which of the following? |
|
A
|
CO32- |
B
|
NH3 |
C
|
H2O |
D
|
ClO4- |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 123 |
Go |
Q:
|
H-C≡C-H
How many π bonds are present between the two carbon atoms in ethyne? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 124 |
Go |
Q:
|
How many total stereoisomers exist for 1-bromo-3-methylcyclohexane? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 125 |
Go |
Q:
|
A structural isomer is noted to have: |
|
A
|
a slightly different molecular formula to the original molecule but the same general configuration of atoms. |
B
|
a difference in the chirality at exactly one chiral center. |
C
|
every stereocenter opposite to the original molecule. |
D
|
identical molecular formula to the original molecule. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 126 |
Go |
Q:
|
A molecule has 16 total stereoisomers (including itself). How many chiral centers would the molecule have? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 127 |
Go |
Q:
|
Meso compounds: |
|
A
|
are optically active. |
B
|
can have a single stereocenter. |
C
|
represent structural isomers of a particular molecular formula. |
D
|
always have a stereoisomer which is optically active. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 128 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is not typically considered an amphipathic molecule? |
|
A
|
phospholipids |
B
|
alcohols |
C
|
long chain hydrocarbons |
D
|
fatty acids |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 129 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is accurate regarding the molecular geometry of silicon tetrachloride and xenon tetrafluoride? |
|
A
|
Silicon tetrachloride and xenon tetrafluoride have the same molecular geometry. |
B
|
Silicon tetrachloride is trigonal planar and xenon tetrafluoride is tetrahedral. |
C
|
Silicon tetrachloride is tetrahedral and xenon tetrafluoride is square planar. |
D
|
Silicon tetrachloride is trigonal planar and xenon tetrafluoride is tetrahedral. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 130 |
Go |
Q:
|
In the following molecule, how many of the nitrogen atoms may be considered chiral centers?
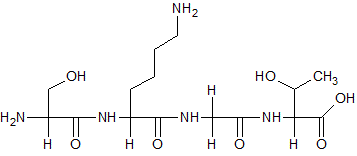 |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 132 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following molecules does not contains a triple bond? |
|
A
|
benzene |
B
|
carbon monoxide |
C
|
nitrogen gas |
D
|
ethyne |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 133 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following changes in molecular geometry occurs in the transition from methane to the methyl cation? |
|
A
|
tetrahedral to planar |
B
|
tetrahedral to bent |
C
|
trigonal pyramidal to tetrahedral |
D
|
tetrahedral to pyramidal |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 135 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following molecules contain sp3d orbitals? |
|
A
|
sulfur hexafluoride |
B
|
phosphorous pentachloride |
C
|
fluoromethane |
D
|
butane |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
| 136 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following molecules correctly lists the magnitudes of the dipole moments of the molecules listed? |
|
A
|
boron trifluoride > boron trichloride > boron tribromide |
B
|
boron trifluoride < boron trichloride < boron tribromide |
C
|
boron trifluoride < boron tribromide < boron trichloride |
D
|
boron trifluoride = boron trichloride = boron tribromide |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | |
|
|
Questions? We're here to help!
Ask Us
|