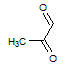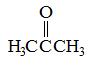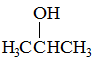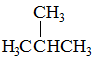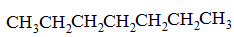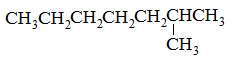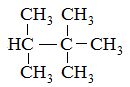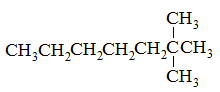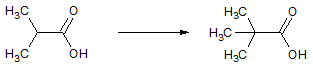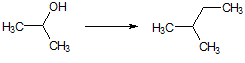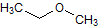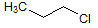|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
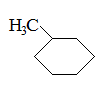
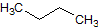
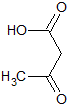
What is the major intermolecular force in the following compound, given that the difference in boiling point between its two stereoisomers is less than 3%?
CH3CH=CHCH2CH3 |
|
A
|
dipole-dipole |
B
|
hydrogen bonding |
C
|
London dispersion |
D
|
ionic |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds would have the highest boiling point? |
|
A
|
2-methylhexane |
B
|
2,4-dimethylpentane |
C
|
2,2,3-trimethylbutane |
D
|
2,2-dimethylpentane |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following molecules would have the highest boiling point? |
|
A
|
CH3CH2CH3 |
B
|
CH3NH2 |
C
|
CH3OH |
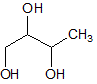
D
|
CH2Cl2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
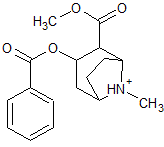
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
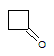
Q:
|
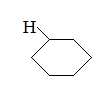
What is the major intermolecular force in the following compound?
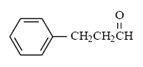 |
|
A
|
dipole-dipole |
B
|
hydrogen bonding |
C
|
London dispersion |
D
|
ionic |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS) is a known denaturant but not a reducing agent. A protein sample is treated with SDS and is denatured. What is the effect of SDS on any disulfide bridges that may be present in the protein? |
|
A
|
The disulfide bridges are broken because SDS oxidizes the disulfide bridges. |
B
|
The disulfide bridges are broken because SDS reduces the disulfide bridges. |
C
|
The disulfide bridges are not broken because SDS strengthens disulfide bridges. |
D
|
The disulfide bridges are not broken because SDS does not affect disulfide bridges. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Protein Structure and Function | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
A polar solid matrix is used for thin layer chromatography. If a nonpolar compound is spotted onto the solid matrix, compare the speed of travel of the compound in the following solvents, from slowest to fastest.
I. diethyl ether
II. hexane
III. methanol
|
|
A
|
III, I, II |
B
|
I, II, III |
C
|
II, I, III |
D
|
III, II, I |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
When 1000 mL of 100% methanol is mixed with 1000 mL of water, less than 1950 mL of liquid results. This is most likely due to |
|
A
|
evaporation of some of both of the liquids prior to mixing |
B
|
evaporation of the solution after mixing, a process which increases the temperature of the solution |
C
|
cooling of the solution due to mixing, resulting in a denser solution with less volume |
D
|
adjustment of the hydrogen bonding of the liquids, resulting in a denser solution and hence, a smaller volume |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
Why is the oxygen-hydrogen absorption of CH3OH such a broad band in the IR reading? |
|
A
|
Rotational energy levels broaden the absorption. |
B
|
Hyperconjugation resonance broadens the absorption. |
C
|
Resonance broadens the absorption. |
D
|
Hydrogen bonding broadens the absorption. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following molecules has the lowest vapor pressure? |
|
A
|
2-propanone |
B
|
2-butanone |
C
|
hexane |
D
|
3-octanone |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
A molecule of DNA is slowly heated. The base pairs are closely examined. It is noted that |
|
A
|
The Adenine and Thymine bonds break before the Guanine and Cytosine bonds. |
B
|
The Guanine and Cytosine bonds break before the Adenine and Thymine bonds. |
C
|
Bond breaking occurs all at a single temperature. |
D
|
Bond breaking occurs at the sites of weakest interaction but has no relation to the individual base pairs. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following atoms are commonly found acting as hydrogen bond acceptors? |
|
A
|
Oxygen |
B
|
Nitrogen |
C
|
Carbon |
D
|
A and B |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
Many mainly-nonpolar carboxylic acids with long alkyl chains are insoluble in water when protonated. With which of the following can they be reacted in order to become soluble? |
|
A
|
HCl |
B
|
NaCl |
C
|
MeOH |
D
|
NaOH |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carboxylic Acids | Redox Reactions | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following interactions result in the specificity and tight binding of the two strands in the DNA double helix? |
|
A
|
London dispersion forces |
B
|
Covalent bonding |
C
|
Hydrogen bonding |
D
|
Dipole-dipole interactions |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which procedure will increases the solubility of KCl in water? |
|
A
|
stirring the solute and solvent mixture |
B
|
increasing the surface area of the solute |
C
|
raising the temperature of the solvent |
D
|
increasing the pressure on the surface of the solvent |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
Large macromolecules have varying solubility in water. Their ability to dissolve is dependent mainly on |
|
A
|
their ability to hydrogen bond with water |
B
|
their ability to hydrogen bond with one another |
C
|
their ability to repel water |
D
|
their ability to repel one another |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 20 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following substances in water will act as the strongest electrolyte? Assume 1 mol of each is mixed into 1 L of water. |
|
A
|
AgCl |
B
|
NaCl |
C
|
Sucrose |
D
|
O2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
A new noble gas X is constructed in the laboratory. The gas is noted to be monatomic. Which of the following intermolecular forces should be present in the gas? |
|
A
|
Dipole-Dipole |
B
|
Hydrogen Bonding |
C
|
London Dispersion |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following substance would you expect to have the lowest melting point? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 23 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds can be expected to have the highest vapor pressure? |
|
A
|
Benzene |
B
|
CH3Cl |
C
|
CH3OH |
D
|
Phenol |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 24 |
Go |
Q:
|
If a small organic molecule forms hydrogen bonds with water it will almost certainly be |
|
A
|
water soluble |
B
|
lipid soluble |
C
|
ionic |
D
|
amphipathic |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 25 |
Go |
Q:
|
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) involves the separation of compounds based on differences in polarity. The compounds interact differently with the solvent and the solid matrix, resulting in a different rate of travel along the solvent front as it wicks along the surface of the solid matrix. Consider a TLC experiment using a solid matrix of silica with diethyl ether as the solvent. Three compounds are dissolved in the ether: tyrosine (structure shown below), benzaldehyde, and phenol (hydroxybenzene). In which order will the compounds follow the solvent front?
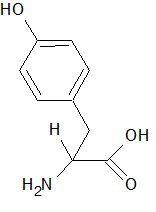 |
|
A
|
phenol, benzaldehyde, tyrosine |
B
|
phenol, tyrosine, benzaldehyde |
C
|
benzaldehyde, tyrosine, phenol |
D
|
benzaldehyde, phenol, tyrosine |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 26 |
Go |
Q:
|
Depending on the nucleotides in a specific strand of DNA, the strands will split at different temperatures. The major cause for this is |
|
A
|
Differences in phosphate amounts on the backbone |
B
|
Differences in G-C and A-T content |
C
|
The width of helix depends on the nucleotide sequence |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Nucleic Acid Structure and Function | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 30 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following has the highest boiling point? |
|
A
|
0.5 M NaCl |
B
|
1.0 M Glucose |
C
|
0.5 M Glucose |
D
|
1.0 M NaCl |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 31 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following elements has the strongest intermolecular force with H2O? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 32 |
Go |
Q:
|
Diols have higher boiling points than their corresponding alcohols with only one hydroxyl group because diols: |
|
A
|
can self-associate to form hydrogen bonds. |
B
|
dissociate more easily in solution. |
C
|
can form intermolecular bonds at two sites of the molecule rather than just one. |
D
|
lack positive charges. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 34 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds is most soluble in supercritical CO2 |
|
A
|
diethyl ether |
B
|
HCl |
C
|
methanol |
D
|
H2O |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 35 |
Go |
Q:
|
A set of protein sequences are given in the tables below. Rank the proteins in increasing order of their ability to form disulfide bridges (covalent bonds between the R-groups of two cysteine sulfhydryl groups).
| Protein |
Sequence |
| 1 |
Alanine-Cysteine-Leucine-Threonine-Phenylalanine-Glutamine-Glycine-Glycine-Asparagine-Cysteine |
| 2 |
Cysteine-Cysteine-Leucine-Threonine-Phenylalanine-Glutamine-Glycine-Glycine-Asparagine-Glycine |
| 3 |
Alanine-Gylcine-Leucine-Threonine-Phenylalanine-Glutamine-Glycine-Glycine-Asparagine-Glycine |
|
|
A
|
I < II < III |
B
|
III < II < I |
C
|
II < III < I |
D
|
III < I < II |
|
|
|
Tags:
Protein Structure and Function | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 36 |
Go |
Q:
|
Alcohols typically have higher boiling points than ketones of similar molecular weight because alcohols |
|
A
|
are more reactive than ketones. |
B
|
are capable of hydrogen bonding. |
C
|
lack symmetry around the carbonyl carbon. |
D
|
lack carbonyl carbon atoms. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Aldehydes and Ketones | Alcohols | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 37 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds will have the highest boiling point? |
|
A
|
CH3OH |
B
|
CH4 |
C
|
CH3Cl |
D
|
CH3SH |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 38 |
Go |
Q:
|
At the critical point of a substance, the liquid state is indistinguishable from the gas, yielding properties of both liquids and gases. For such a fluid of SO2, which of the following would most readily be dissolved? |
|
A
|
KCl |
B
|
NH4OH |
C
|
H3COCH3 |
D
|
NaNO3 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 39 |
Go |
Q:
|
Carboxyl groups have higher boiling points than acid halides because they are capable of self-associating with hydrogen bonds to form dimeric associations. Acid halides, however, are only capable of receiving hydrogen bonds, not donating them, and cannot self-associate with hydrogen bonds. The structure on acid halides and carboxylic acids that receives hydrogen bonds is the: |
|
A
|
carbon of the carbonyl group |
B
|
oxygen of the carbonyl group |
C
|
oxygen of the hydroxyl group |
D
|
carbon of the R-group |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | Carboxylic Acids | Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 40 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is the strongest intermolecular force? |
|
A
|
Covalent bond |
B
|
Dipole-dipole interactions |
C
|
Hydrogen bonding |
D
|
London dispersion force |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 41 |
Go |
Q:
|
The boiling point of methane is 110 K while the boiling point of germane, GeH4 is 185 K. This difference in boiling points is primarily attributable to which of the following? |
|
A
|
The difference in electronegativity between carbon and germanium. |
B
|
The difference in polarity of the bonds between C-H and Ge-H. |
C
|
The difference in size between carbon and germanium. |
D
|
The difference in ionization energy between carbon and germanium. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 42 |
Go |
Q:
|
The difference in boiling points between methanol and chloromethane can be primarily attributed to which of the following differences? |
|
A
|
Hydrogen bonding |
B
|
Strength of the dipoles |
C
|
London dispersion forces |
D
|
Isotope stability |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 43 |
Go |
Q:
|
Protein-protein interactions are usually reversible and temporary. These interactions are mediated by a number of different mechanisms. Which of the following is NOT found in such temporary protein-protein interactions?
I. Hydrophobic interactions
II. Ionic bonds
III. Covalent bonds |
|
A
|
I and II only |
B
|
III only |
C
|
I and III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 44 |
Go |
Q:
|
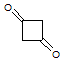
Which of the following accounts for the majority of the difference in melting points between the two compounds shown below?
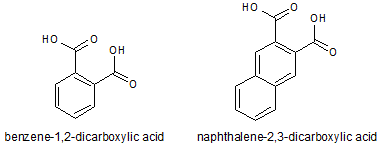 |
|
A
|
Hydrogen bonding |
B
|
Permanent dipole interactions |
C
|
Covalent bonding |
D
|
London dispersion forces |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 45 |
Go |
Q:
|
The compound CH3CHClCH2OH will have which of the following intermolecular forces?
I. Hydrogen bonding
II. Dipole-dipole interaction
III. London dispersion force |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
I and II only |
C
|
II and III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 47 |
Go |
Q:
|
HCl has a lower boiling point than HI. The reason for this can be best attributed to which of the following? |
|
A
|
HCl is more polar than HI |
B
|
HCl is less polar than HI |
C
|
HCl is much larger than HI |
D
|
HCl is much smaller than HI |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 48 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which is the correct ordering for the following solutions when listed from highest boiling point to lowest boiling point? Note the Ka of HF is 7.2 x 10-4 and the remaining solutes are highly water-soluble.
0.05 m Mg(NO3)2
0.10 m sucrose
0.15 m KCl
0.10 m NaI
0.05 m HF |
|
A
|
Mg(NO3)2, KCl, NaI, HF, sucrose |
B
|
KCl, NaI, Mg(NO3)2, sucrose, HF
|
C
|
NaI, KCl, Mg(NO3)2, sucrose, HF |
D
|
KCl, Mg(NO3)2, NaI, sucrose, HF |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 49 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is LEAST likely to impact the boiling point of a solvent? |
|
A
|
The number of hydrogen bonds it can form |
B
|
The molecular weight of the molecule |
C
|
The presence of d-orbitals in any of its atoms |
D
|
The presence of charged species on the atom |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 50 |
Go |
Q:
|
The pungent smell of burning hair is due to the large concentration of sulfur in keratin. Which of the following describes the role of the sulfur? |
|
A
|
It is concentrated in hair along with other environmental toxins. |
B
|
It is present in disulfide bridges in keratin. |
C
|
It is part of the carbohydrate structure of the hair. |
D
|
It acts as a pigment for the keratin in the hair. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Protein Structure and Function | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 51 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds would not have hydrogen bonds? |
|
A
|
CH3CH2CH2OH |
B
|
(CH3)3N |
C
|
CH3NH2 |
D
|
HF |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 52 |
Go |
Q:
|
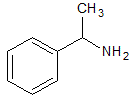
The solubility in water of the compound above increases dramatically when which of the following occurs? |
|
A
|
The methyl group is replaced with an ethyl group |
B
|
The amine is methylated |
C
|
The C-CH3 group is replaced with C=O to make an amide |
D
|
The pH of the solution is lowered below the pKa of the compound |
|
|
|
Tags:
Acid/Base Equilibria | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 53 |
Go |
Q:
|
TLC is performed on samples at different time points of a reaction. The matrix is a polar stationary phase and the mobile phase used is a 1:10 ratio of ethyl acetate:diethyl ether. Blots in early time points show a compound with an Rf value of 0.38 slowly diminishing and being replaced with a compound with an Rf value of 0.22. Which of the following reactions could have taken place? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 54 |
Go |
Q:
|
The boiling point of hydrogen gas is 20 K while the boiling point of helium is 4 K. This difference in boiling points can be attributed to which of the following? |
|
A
|
Helium is a noble gas. |
B
|
Hydrogen has stronger hydrogen bonds than helium. |
C
|
Helium lacks a dipole. |
D
|
Hydrogen gas has stronger van der Waals interactions than helium. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 55 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following bond types is the strongest intermolecular force? |
|
A
|
Van der Waals |
B
|
Dipole-dipole |
C
|
Hydrogen bonding |
D
|
Covalent |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 56 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds can be expected to have the highest boiling point? |
|
A
|
CH3OH |
B
|
CH3F |
C
|
CH3NH2 |
D
|
CH3CH2CH3 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 57 |
Go |
Q:
|
The reason that xenon has a higher boiling point than krypton is due to: |
|
A
|
ionic forces. |
B
|
dipole-dipole interactions. |
C
|
hydrogen bonding. |
D
|
Van der waals forces. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 58 |
Go |
Q:
|
Methyl fluoride is found to have a significantly lower boiling point than that of fluorobenzene. Which of the following accounts for the majority of the difference in melting points between these two compounds? |
|
A
|
Hydrogen bonding |
B
|
London dispersion forces |
C
|
Permanent dipole interactions |
D
|
Covalent bonding |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 60 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the molecule below, which of the following best describes its polarity, (if any)?
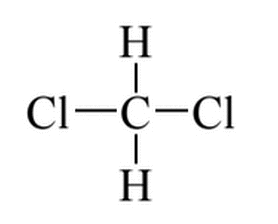 |
|
A
|
Polar with an overall molecular dipole moment
|
B
|
Nonpolar with an overall molecular dipole moment
|
C
|
Polar without an overall molecular dipole moment
|
D
|
Nonpolar without an overall molecular dipole moment
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Structure | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 61 |
Go |
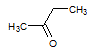
Q:
|
Given the molecules below, which of the following best explains which molecule has the higher boiling point and why? Note that the negligible difference in molecular weight can be treated as non-influential to the boiling point difference.
 |
|
A
|
The left molecule because there are no London dispersion forces present
|
B
|
The left molecule because there are stronger dipole-dipole interactions present
|
C
|
The right molecule because of the resonance capabilities of the oxygen atom
|
D
|
The right molecule because there are stronger dipole-dipole interactions present
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 62 |
Go |
Q:
|
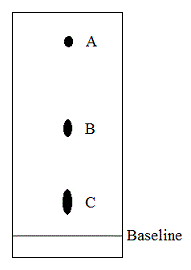
Paper chromatography is run on a wine sample with blots A, B, and C corresponding to lactic, malic, and tartaric acids, respectively. Which of the conclusion regarding the three acids is true based on this information? |
|
A
|
Tartaric acid is the least polar of the acids. |
B
|
Malic acid is more polar than tartaric acid and less polar than lactic acid. |
C
|
Lactic acid is the least polar of the acids. |
D
|
Lactic acid is more polar than malic acid and less polar than tartaric acid. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | Chemistry Laboratory Techniques | |
|
| 64 |
Go |
Q:
|
How would a decrease in the pH of a solution affect the volatility of decanoic acid? |
|
A
|
The volatility decreases until the pH equals the pKa at which point the volatility increases. |
B
|
The volatility increases until the pH equals the pKa at which point the volatility decreases. |
C
|
The volatility continues to increase as the pH decreases. |
D
|
The volatility continues to decrease as the pH decreases. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | Carboxylic Acids | |
|
| 65 |
Go |
Q:
|
What difference would be expected between 1-butanol and 1,2-butanediol? |
|
A
|
1,2-butanediol would have higher volatility than 1-butanol. |
B
|
1,2-butanediol would a lower molecular weight than 1-butanol. |
C
|
1,2-butanediol would have a higher boiling point than 1-butanol. |
D
|
1,2-butanediol would have lower solubility in water than 1-butanol. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | Alcohols | |
|
| 66 |
Go |
Q:
|
van der Waals forces increase with: |
|
A
|
increased size of a molcule. |
B
|
decreased size of a molecule. |
C
|
increased polarity of a molecule. |
D
|
increased number of branch points in a molecule. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 67 |
Go |
Q:
|
Hydrogen bonds can be considered a form of: |
|
A
|
dipole-dipole interactions. |
B
|
ionic bonds. |
C
|
covalent bonds. |
D
|
van der Waals forces. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 68 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is considered a dipole-dipole interaction?
I. hydrogen bond
II.London dispersion force
III. ionic bond |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
I and II only |
C
|
II and III only |
D
|
I, II and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 69 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following molecules would be expected to have the lowest boiling point? |
|
A
|
propane |
B
|
propanol |
C
|
butane |
D
|
2-butanol |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | Alcohols | |
|
| 70 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following structures do not participate in hydrogen bonding? |
|
A
|
DNA |
B
|
alpha helical structures of proteins |
C
|
branched hydrocarbons |
D
|
ice |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 71 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following molecules are considered polar?
I. carbon dioxide
II. phosphate trifluoride
III. hydrogen fluoride
IV. methene
|
|
A
|
II only |
B
|
II and III only |
C
|
III only |
D
|
I and III only |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 72 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following intermolecular forces contributes to the boiling point of the following molecule:

I. dipole-dipole
II. london dispersion
III. ionic
IV. hydrogen bonding |
|
A
|
I and II only |
B
|
I, II and IV only |
C
|
II only |
D
|
I, II, III, and IV |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | |
|
|
Questions? We're here to help!
Ask Us
|