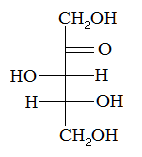|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
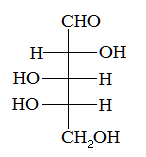
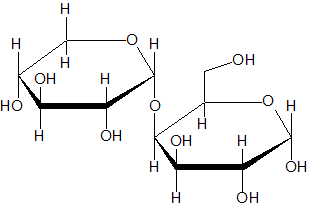
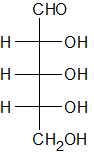
Which of the following compounds is an L-aldopentose? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
The compound with molecular formula
C6H12O6 is most
commonly a(n) |
|
A
|
glucanose |
B
|
polysaccharide |
C
|
furanose |
D
|
pyranose |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
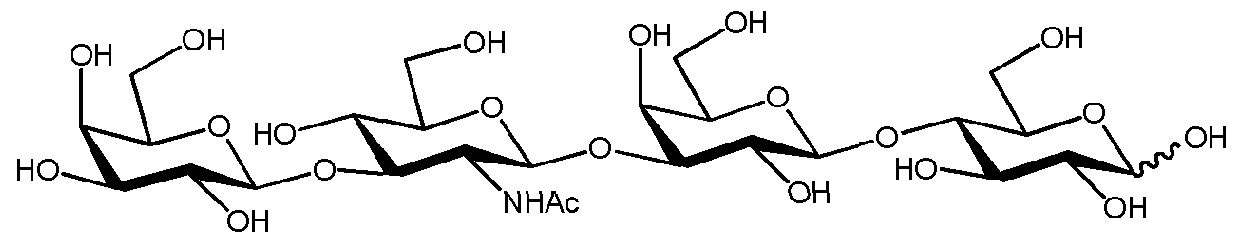
Which of the following molecules does not contain at least one glycosidic bond? |
|
A
|
Sucrose |
B
|
Maltose |
C
|
Glycogen |
D
|
Ribose |
|
|
|
Tags:
Molecular Bonding | Carbohydrates | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
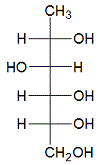
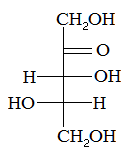
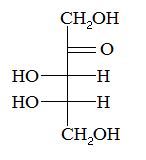
The compound above is an example of a |
|
A
|
ketohexose |
B
|
aldohexose |
C
|
ketopentose |
D
|
none of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is an example of a dimer? |
|
A
|
Glucose |
B
|
Maltose |
C
|
Starch |
D
|
Cellulose |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following statements regarding a β-pyranose is false? |
|
A
|
The is only one anomeric carbon. |
B
|
The formation of the ring results in an intramolecular hemiacetal. |
C
|
Two different chair conformations are possible. |
D
|
It can only be formed from a hexose. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following pairs of monosaccharides are anomers? |
|
A
|
β-D-glucopyranose and β-D-mannopyranose |
B
|
β-D-glucopyranose and α-D-mannopyranose |
C
|
β-D-glucopyranose and α-D-glucopyranose |
D
|
β-D-glucopyranose and β-L-glucopyranose |
|
|
|
Tags:
Atomic & Electronic Structure | Carbohydrates | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
A PET (Positron Emission Tomography) scan typically uses fludeoxyglucose, a synthetic radioactive glucose analog that is imported into cells but cannot be metabolized until after radioactive decay. On a scan image, regions of high radioactivity would directly be indicative of |
|
A
|
high volume of blood flow. |
B
|
high rate of cell division. |
C
|
high metabolic activity. |
D
|
high rate of apoptosis. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | Glycolysis, Gluconeogenesis, PPP | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
Beta-D-glucose has 5 stereocenters with the designations: 1S, 2R, 3S, 4S, 5R. Which of the following stereocenter designations below is the enantiomer of Beta-D-glucose? |
|
A
|
1R, 2S, 3R, 4R, 5S |
B
|
1S, 2S, 3S, 4R, 5R |
C
|
1R, 2S, 3S, 4R, 5R |
D
|
1R, 2S, 3R, 4S, 5S |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
The primary difference between furanose and pyranose rings is: |
|
A
|
furanose is a five-membered ring while pyranose is a six-membered ring |
B
|
furanose is made from a ketose while pyranose is made from an aldose |
C
|
furanose is made from a pentose while pyranose is made from a hexose |
D
|
None of the above. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
α-D-glucopyranose and β-D-glucopyranose are:
I. Anomers
II. Epimers
III. Diastereomers |
|
A
|
III only |
B
|
I and III only |
C
|
I and II only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | Molecular Structure | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
Kiliani-Fischer synthesis is a method converting a monosaccharide into a monosaccharide with one more carbon atom. Because the mechanism is not stereospecific, two epimers are produced from each monosaccharide. If a sample of D-glyceraldehyde, a triose, were used and a series of Kiliani-Fischer syntheses were applied, what proportion of all hexoses would be glucose? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is NOT correct about carbohydrates in cells?
|
|
A
|
They are involved in cell-to-cell recognition
|
B
|
They can be organic catalysts
|
C
|
They can act as binding sites for proteins
|
D
|
They can serve as energy stores in animal cells |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | Membrane Transport and Signalling | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
α-glucose and β-glucose are different at the: |
|
A
|
C1 carbon. |
B
|
C2 carbon. |
C
|
C3 carbon. |
D
|
C4 carbon. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is NOT true regarding an endothermic chemical reaction such as joining together glucose and fructose to form sucrose? |
|
A
|
The reaction requires an input of energy
|
B
|
With a large amount of entropy, an exergonic reaction can result |
C
|
The reaction releases energy
|
D
|
The energy used in bond-breaking reactions is greater than the energy released in bond-making products |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | Carbohydrates | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
Similar to those found in carbohydrates, which type of protein linkage is most similar to a glycosidic linkage? |
|
A
|
Alpha helix
|
B
|
Beta sheet |
C
|
Disulfide bond
|
D
|
Peptide bond |
|
|
|
Tags:
Protein Structure and Function | Carbohydrates | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
In normal E. coli, which of the following conditions would be the most ideal for the energy-efficient transcription of the lacZ and lacY genes of the lac operon? |
|
A
|
Low glucose, low lactose
|
B
|
High glucose, low lactose
|
C
|
Low glucose, high lactose
|
D
|
High glucose, high lactose
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Gene Expression in Prokaryotes | Carbohydrates | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
In untreated diabetics, excess glucose in the blood is due to incomplete reabsorption (normally done by transporters present in the nephrons of the kidney) and subsequent excretion in the urine. Which of the following best describes this effect?
|
|
A
|
The transporters are inhibited by high levels of glucose
|
B
|
The Vmax of the transporter is reached at lower blood glucose levels
|
C
|
The binding affinity of these transporters is increased in diabetics
|
D
|
The binding capacity of the transporters has been exceeded
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Membrane Transport and Signalling | Renal System | Protein Structure and Function | Carbohydrates | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following best describes the pyranose below?
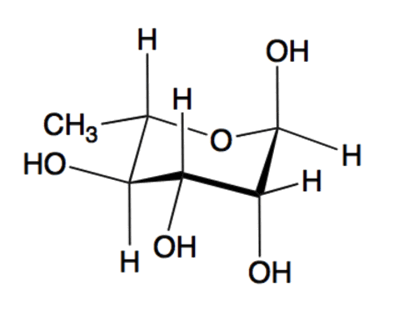 |
|
A
|
D-sugar, α-anomer
|
B
|
D-sugar, β-anomer
|
C
|
L-sugar, α-anomer
|
D
|
L-sugar, β-anomer
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
| 23 |
Go |
Q:
|
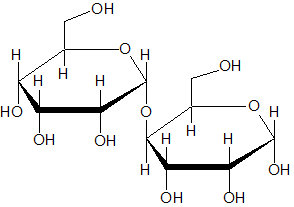
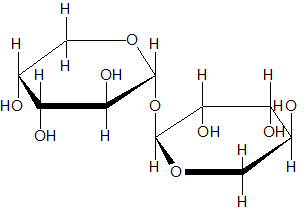
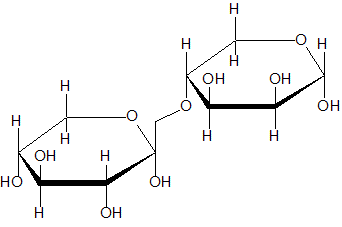
Which of the following disaccharides is NOT a reducing sugar? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
| 25 |
Go |
Q:
|
Cyclic carbohydrates can be reducing sugars only if: |
|
A
|
they have a free -H group. |
B
|
they have a free aldehyde or ketone group. |
C
|
they are in an α linkage. |
D
|
they are disaccharides. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
| 26 |
Go |
Q:
|
The conversion of a disaccharide to a monosaccharide is what type of reaction? |
|
A
|
condensation |
B
|
hydrolysis |
C
|
deacetylation |
D
|
tautomerization |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
| 27 |
Go |
Q:
|
The Tollens' test will yield a shiny silver mirror on the glass vial containing the reaction if what type of sugar is added? |
|
A
|
reducing sugar |
B
|
non-reducing sugar |
C
|
any disaccharide |
D
|
any non-monosaccharide |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | Organic Chemistry Reactions | |
|
| 28 |
Go |
Q:
|
The digestion of carbohydrates starts in the: |
|
A
|
oropharynx. |
B
|
esophagus. |
C
|
stomach. |
D
|
duodenum. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
| 29 |
Go |
Q:
|
D-glucose and L-glucose differ in the stereochemistry of how many chiral centers? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
| 30 |
Go |
Q:
|
Two sugar molecules are found to be epimers. This implies they: |
|
A
|
have identical chemical properties. |
B
|
have different arrangements of atoms within the molecule. |
C
|
differ in only one stereocenter. |
D
|
differ in functional groups but otherwise have the same atomic structure. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
| 31 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following structures would not be expected to be a common structure found in polysaccharides? |
|
A
|
glycosidic linkages |
B
|
monosaccharide units |
C
|
hydroxyl -OH groups |
D
|
amine and carboxyl groups |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
| 32 |
Go |
Q:
|
Two epimers are studied in a laboratory and their respective stereocenters are reviewed. How many stereocenters may differ between the two molecules?
I. one
II. two
III. three or more |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
I and II only |
C
|
II only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
| 33 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is a disaccharide? |
|
A
|
starch |
B
|
glucose |
C
|
maltose |
D
|
cellulose |
|
|
|
Tags:
Carbohydrates | |
|
|
Questions? We're here to help!
Ask Us
|