|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following ways would not increase the solubility of a gas in a liquid? |
|
A
|
Increase pressure of the system |
B
|
Decrease temperature of the system |
C
|
Increase temperature of the system |
D
|
Decrease volume of the system |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Gases | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following compounds is expected to have the lowest vapor pressure? |
|
A
|
CH3OCH3 |
B
|
CH3CH2OH |
C
|
CH3CH2CH3 |
D
|
CH3Cl |
|
|
|
Tags:
Alcohols | Gases | Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
Using the ideal gas law, which of the following statements is true about a closed system? (where n is held constant) |
|
A
|
At constant temperature, an increase in pressure will result in an increase in volume. |
B
|
At constant temperature, an increase in pressure will result in a decrease in volume. |
C
|
At constant pressure, an increase in volume will result in a decrease in temperature. |
D
|
At constant pressure, a decrease in volume will result in an increase in temperature. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
Condensation of water in the atmosphere requires a nucleation point for clouds. Which of the following substances functions as a most effective nucleation point? |
|
A
|
ozone |
B
|
dust |
C
|
NOx |
D
|
sand |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
The Haber process is a common mechanism for creating ammonia from nitrogen and hydrogen gas. The reaction is as follows: N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) + heat. There is a large closed vat in which the Haber process occurs. Predict what would happen if the vat were to mechanically and instantly decrease in size, all else remaining constant. |
|
A
|
The amount of nitrogen gas in the vat would increase. |
B
|
There would be a significant decrease in temperature. |
C
|
There would be an increase the amount of ammonia. |
D
|
Temperature would remain constant. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
Arrange the following substances in terms of increasing molar entropy at standard room temperature and pressure: Ca(s), Cl2(g), Cl2(l), CaCl2(s) |
|
A
|
Cl2(g), Cl2(l), Ca(s), CaCl2(s) |
B
|
Cl2(g), Cl2(l), CaCl2(s), Ca(s) |
C
|
CaCl2(s), Ca(s), Cl2(l), Cl2(g) |
D
|
Ca(s), CaCl2(s), Cl2(l), Cl2(g) |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Fluids | Gases | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
A researcher pumps a known gas into an empty cylinder, compressing the gas, and, as a consequence, increasing the temperature of the cylinder. In order to determine the amount of gas pumped into the cylinder, which of the following methods would be most effective? |
|
A
|
use a pressure gauge and calculate the amount of gas based on the pressure and the known volume |
B
|
measure the difference in mass before and after filling |
C
|
measure the change in temperature before and after filling |
D
|
use an ultrasonic device to measure the density of the gas inside the cylinder |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
The balloon industry is experimenting with different heavier gases which can be used for non-floating balloons. The two gases are labeled gas A and gas B. Gas A is about 9 times heavier than gas B. Gas A was placed in a standard balloon and tested to effusion speed. The gas was found to have a effusion speed of k. What is the expected effusion speed of gas B? Assume that the mass of gas A per mol is M g/mol. |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
The cylindrical container is closed to the atmosphere and is pressurized. What is the pressure inside the container if the atmospheric pressure is 735mmHg?
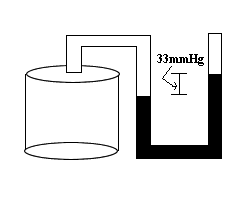 |
|
A
|
702 mmHg |
B
|
33 mmHg |
C
|
735 mmHg |
D
|
768 mmHg |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
A vertical tube stands with its top end sealed and its bottom end submerged in water (ρ = 1.0 g/mL). If a vacuum is drawn inside the tube, at which atmospheric pressure will the vertical height in the tube be greatest? |
|
A
|
0.5 atm |
B
|
1 atm |
C
|
1.5 atm |
D
|
All are the same; a vacuum exists inside the tube regardless of the atmospheric pressure outside the tube.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
In a gas, assume that the mass of each molecule is 10-5 kg and each molecule travels at 1 m/s. Utilizing the de Broglie wavelength equation λ = h/(mv), what is the wavelength of each gas particle? Assume that Planck's Constant is h = 7 x 10-34. |
|
A
|
7 x 1029 m |
B
|
7 x 10-29 m |
C
|
7 x 10-30 m |
D
|
7 x 10-31 m |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Electromagnetics | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
A gas is observed to exhibit an aggregation of its molecules into clumps of different sizes. Each clump contains 2k molecules, for some integer k, i.e. the size of clump increases by doubling. How will a clump with 2k molecules effuse out of a small hole in comparison to one molecule? |
|
A
|
2k/2 times faster |
B
|
2k/2 times slower |
C
|
2-k/2 times faster |
D
|
2-k/2 times slower |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
Why is the oxygen-hydrogen absorption of CH3OH such a broad band in the IR reading? |
|
A
|
Rotational energy levels broaden the absorption. |
B
|
Hyperconjugation resonance broadens the absorption. |
C
|
Resonance broadens the absorption. |
D
|
Hydrogen bonding broadens the absorption. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
A chemical reaction occurs within a sealed container. If the moles of gas double and the volume is halved, what is the magnitude of the pressure assuming temperature remains constant?
|
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
A gas is initially at a pressure of P1 and at a volume of V1. What is the volume of the gas if the pressure suddenly changes to P2?
|
|
A
|
P1V1/P2 |
B
|
P1P2/V1 |
C
|
P2V1/P1 |
D
|
P2/P1V1 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following gases most likely has the highest heat capacity? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
A phase diagram depicts the conditions under which a substance is in its solid, liquid, or gaseous state. What are the axes of the phase diagram? |
|
A
|
temperature (y-axis) vs. pressure (x-axis) |
B
|
pressure (y-axis) vs. temperature (x-axis) |
C
|
temperature (y-axis) vs. vapor pressure (x-axis) |
D
|
vapor pressure (y-axis) vs. temperature (x-axis) |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Gases | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular compound has a molecular mass of 50. How many times faster will it diffuse than a compound whose molecular mass is 200?
|
|
A
|
1 |
B
|
√2 |
C
|
2 |
D
|
impossible to determine from the information given |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
Under which conditions are gases most soluble in water? |
|
A
|
high pressure and high temperature |
B
|
high pressure and low temperature |
C
|
low pressure and high temperature |
D
|
low pressure and low temperature |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 20 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the mechanism of oxygen transport from the lungs into the bloodstream? |
|
A
|
Osmosis |
B
|
Simple Diffusion |
C
|
Active transport |
D
|
Facilitated diffusion |
|
|
|
Tags:
Respiratory System | Circulatory System | Gases | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given three samples of identical mass, which is expected to have the largest volume? |
|
A
|
Solid |
B
|
Liquid |
C
|
Gas |
D
|
They should all have the same volume since they have the same mass. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Gases | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
A gas decomposes via zero order reaction to twice the number of moles. If the first half-life of the reaction is complete in 20 seconds, and the volume of the reaction system is 1 L, what will the volume be after 40 seconds? Assume constant temperature and pressure. |
|
A
|
1.5 L |
B
|
1.75 L |
C
|
2 L |
D
|
The volume cannot be determined from the information given. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Chemical Kinetics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 23 |
Go |
Q:
|
A new noble gas X is constructed in the laboratory. The gas is noted to be monatomic. Which of the following intermolecular forces should be present in the gas? |
|
A
|
Dipole-Dipole |
B
|
Hydrogen Bonding |
C
|
London Dispersion |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Intermolecular Forces | |
|
| 24 |
Go |
Q:
|
When light travels from air to water, which of the following occurs? |
|
A
|
Frequency changes |
B
|
Wavelength changes |
C
|
Energy changes |
D
|
Energy decreases but only to a minimal extent |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Gases | Electromagnetics | |
|
| 25 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is the closest approximation to the value of Avogadro's constant? |
|
A
|
6.48 x 1013 |
B
|
6.67 x 10-11 |
C
|
6.63 x 10-34 |
D
|
6.02 x 1023 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 26 |
Go |
Q:
|
A gas has a volume of 3 L at 600 torr. What is the volume of the gas at 800 torr, all else being equal? |
|
A
|
9/4 L |
B
|
4/9 L |
C
|
6/8 L |
D
|
8/6 L |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 27 |
Go |
Q:
|
Under standard conditions, water will pass from solid to gas through a liquid intermediate. Under which conditions will water pass directly from solid to gas without a liquid intermediate? |
|
A
|
Increased humidity |
B
|
Increased salinity |
C
|
Decreased pressure |
D
|
Decreased gravity |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Gases | |
|
| 28 |
Go |
Q:
|
The molecular weight of a gas is 4 times greater than that of another gas. What is the relative rate of diffusion between the two gases? (i.e. The heavier gas diffuses ____ times as fast as the lighter gas). |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 29 |
Go |
Q:
|
A gas bubble is located at the bottom of a water-filled container. As the bubble is rising toward the surface, which of the following occurs? Assume the gas does not dissolve into the water. |
|
A
|
The bubble becomes smaller. |
B
|
The water level rises. |
C
|
The bubble becomes larger. |
D
|
The water level lowers. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Gases | |
|
| 30 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which is a feature of noble gases? |
|
A
|
They are polyatomic |
B
|
They are unstable |
C
|
They have a low boiling temperature |
D
|
Their outer shell of electrons is relatively empty |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Periodic Table | |
|
| 31 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which element can form diatomic, non polar molecules? |
|
A
|
Nitrogen |
B
|
Manganese |
C
|
Sodium |
D
|
Helium |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Periodic Table | |
|
| 32 |
Go |
Q:
|
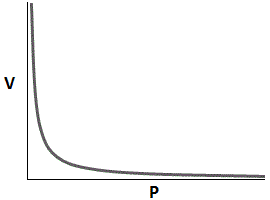
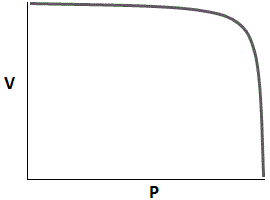
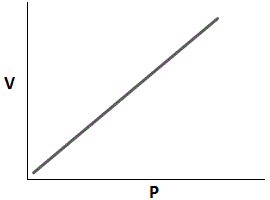
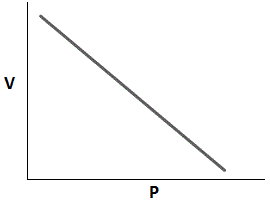
Which of the following graphs accurately depicts the relationship between volume and pressure of a closed system assuming temperature remains constant? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 33 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given 1 mole of CH4, which of the following relationships is true, given P is the pressure, V is the volume, R is the ideal gas constant, and T is the absolute temperature? |
|
A
|
PV/RT = 1 |
B
|
PR/T = V |
C
|
PT/R = V |
D
|
RV/PT = 1 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 34 |
Go |
Q:
|
An ideal gas does work on the surroundings and undergoes an expansion from 10 L to 20 L. The external pressure is constant at 1 atm. The surroundings did 1000 work on the gas. What was the change in the internal energy of the gas? (1 L*atm = 100 J) |
|
A
|
-1000 J |
B
|
1000 J |
C
|
0 J |
D
|
2000 J |
|
|
|
Tags:
Energy & Work | Gases | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 35 |
Go |
Q:
|
Equal moles of the 4 different gases are placed in a closed container with a small pinhole opening in its side, they are: propane, methane, ethane, and chloromethane. After a short period has passed, which gas would have the lowest mole fraction? |
|
A
|
Propane |
B
|
Methane |
C
|
Ethane |
D
|
Chloromethane |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 36 |
Go |
Q:
|
A gaseous hydrocarbon at STP occupies 44.8 L of space. If it is measured that there is 116 g of the gas, what is the hydrocarbon? |
|
A
|
C3H8
|
B
|
C4H10 |
C
|
C5H12 |
D
|
C5H10 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Periodic Table | |
|
| 37 |
Go |
Q:
|
An unknown substance in a solid state is pressurized while keeping its temperature constant. As the pressure increases, the substance eventually converts into a liquid state. This observation suggests |
|
A
|
the solid of the substance sinks in its liquid. |
B
|
the solid of the substance is neutrally buoyant in its liquid. |
C
|
the solid of the substance floats on its liquid. |
D
|
impossible to tell from the given information. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Gases | |
|
| 38 |
Go |
Q:
|
Two gasses, Gas A and Gas B, are in a thinly-lined chamber and have masses MA and MB, respectively. If Gas B effuses 4 times faster than Gas A, what is the mass of Gas A? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 39 |
Go |
Q:
|
Pure HCl and HBr can both be found in gaseous states. The two gasses are placed in identical molar amounts into chambers of equal volumes. Assuming the two molecules are only equal in size, what is the relationship between the pressures of the different compounds? |
|
A
|
HCl has a lower pressure because it is more polar than HBr and its attractive forces cause less pressure against the chamber walls. |
B
|
HCl has a higher pressure because it is more polar than HBr and its attractive forces cause more pressure against the chamber walls. |
C
|
HBr has a lower pressure because it is more polar than HCl and its attractive forces cause less pressure against the chamber walls. |
D
|
HBr has a higher pressure because it is more polar than HCl and its attractive forces cause more pressure against the chamber walls. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 40 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following statements holds true for any given substance at its triple point? |
|
A
|
At the triple point, if pressure is increased, the substance will enter the liquid phase |
B
|
At the triple point, if pressure is increased, the substance will enter the solid phase |
C
|
At the triple point, if pressure is increased, the substance will enter the gas phase |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Gases | |
|
| 41 |
Go |
Q:
|
An air bubble is released in water at a depth of 100 m. Which of the following statements is false regarding the bubble as it rises to the surface? |
|
A
|
The density of the bubble will decrease as it rises |
B
|
The bubble will maintain its volume as it rises |
C
|
The bubble will accelerate upwards as it rises |
D
|
The pressure on the bubble decreases as it rises |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Gases | |
|
| 42 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which does NOT hold true for the following phase diagram?
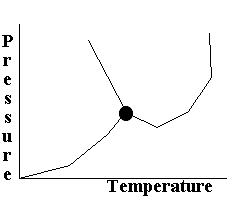
|
|
A
|
At the triple point, all three states of matter coexist |
B
|
At temperatures greater than the triple point temperature, there can exist both solid and liquid forms |
C
|
There exists a temperature/pressure combination at which only gas form can be found |
D
|
All of the above hold true |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Gases | |
|
| 43 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following best explains the unreactivity of noble gasses? |
|
A
|
They possess an even number of electrons which is a stable configuration. |
B
|
Their proton:neutron ratio is optimal for stability. |
C
|
They have complete valence shells and do not easily accept or donate electrons to form bonds. |
D
|
Noble gasses lack d orbitals, thereby substantially increasing their stability. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Periodic Table | |
|
| 44 |
Go |
Q:
|
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
What volume of gas is produced by the reaction above if 2 moles of HCl are used with excess Zn at STP? |
|
A
|
1 L |
B
|
2 L |
C
|
11.2 L |
D
|
22.4 L |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Stoichiometry | |
|
| 45 |
Go |
Q:
|
The plot of air pressure versus elevation shows a nonlinear decrease while the plot of water pressure versus depth is linear. This difference is primarily due to |
|
A
|
the incompressibility of water but the compressibility of air. |
B
|
the fact that water is denser than air. |
C
|
the fact that air is more fluid than water. |
D
|
the differences in elevations measured in air height versus water depth. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Gases | |
|
| 46 |
Go |
Q:
|
A porous balloon allowing gas exchange is filled with an equal molar amount of hydrogen gas and oxygen. Which of the following statements is true after after some time? |
|
A
|
The mole fraction of hydrogen in the balloon is greater than 0.5 |
B
|
Oxygen leaves the hole at a faster rate than hydrogen |
C
|
The mole fraction of hydrogen outside of the balloon is greater than 0.5 |
D
|
The mole fraction of oxygen in the balloon is greater than 0.5 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 47 |
Go |
Q:
|
How much work in Joules is done when a balloon expands from a volume of 2 L to a volume of 5 L against a constant pressure of 12 atm? Note: assume 1 L·atm = 100 J. |
|
A
|
-3600 J |
B
|
400 J |
C
|
3600 J |
D
|
6000 J |
|
|
|
Tags:
Energy & Work | Gases | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 48 |
Go |
Q:
|
Dry ice (solid CO2) has a density of 1.5 g/cm3. By what factor does the volume change during the sublimation of dry ice to gaseous CO2 at STP? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Periodic Table | |
|
| 49 |
Go |
Q:
|
Phase transitions typically involve encountering a barrier with two distinct phases during the transition where a material must convert from one phase directly into another. This can be avoided through which of the following transitions? |
|
A
|
Gas to liquid |
B
|
Solid to liquid |
C
|
Solid to gas |
D
|
There is no way to avoid a phase transition barrier. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Gases | |
|
| 50 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the energy required to raise the temperature of 100 g of water from 50 °C to its boiling point and to completely vaporize it? (Assume the heat capacity of water is 4.2 J/g·K and the ΔHvaporization of water is 2260 kJ/kg) |
|
A
|
21 kJ |
B
|
247 kJ |
C
|
2281 kJ |
D
|
21226 kJ |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Gases | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 51 |
Go |
Q:
|
Gases will behave LEAST like ideal gases under conditions of: |
|
A
|
low pressure and high temperature |
B
|
low pressure and low temperature |
C
|
high pressure and high temperature |
D
|
high pressure and low temperature |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 52 |
Go |
Q:
|
A coal mine [pure C(s)] catches fire and is sealed at all entrances to stop the fire from spreading. Assuming the only product of combustion is CO2 and the seals allow no gasses to escape, which of the following is(are) true?
I. The pressure increases in the chamber are due to the temperature increases
II. The pressure increases in the chamber are due to the increase in the number of moles of gas in the chamber
III. the pressure increases in the chamber are due to the expanding walls of the chamber |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
I and II only |
C
|
II and III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 53 |
Go |
Q:
|
MgH2 + 2H2O → 2 H2 + Mg(OH)2
How many moles of MgH2 would need to be decomposed in the reaction above in order to produce 11.2 L of H2 gas at STP? |
|
A
|
1 mole |
B
|
1/4 mole |
C
|
1/2 mole |
D
|
2 moles |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Solutions | |
|
| 54 |
Go |
Q:
|
Zn + HCl → ZnCl2 + H2
Consider the above unbalanced reaction. How many mL of a 4 M solution of HCl would be required to produce 22.4 L of H2 gas at STP?
|
|
A
|
125 mL |
B
|
250 mL |
C
|
500 mL |
D
|
750 mL |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Stoichiometry | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 55 |
Go |
Q:
|
The nonlinear relationship between pressure and depth for air is primarily due to the: |
|
A
|
compressibility of air. |
B
|
low viscosity of air. |
C
|
lack of intermolecular forces in air. |
D
|
low molecular weight of the molecules in air. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 56 |
Go |
Q:
|
If the number of moles of gas in a closed chamber are doubled, by what proportion would the volume need to change to keep the pressure constant? Assume temperature is held constant. |
|
A
|
Decrease by a factor of 4 |
B
|
Decrease by a factor of 2 |
C
|
Increase by a factor of 2 |
D
|
Increase by a factor of 4 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 57 |
Go |
Q:
|
In the reaction below, if 3 moles of HCl react completely with with excess NaHCO3, how much gas is evolved at STP?
HCl (aq) + NaHCO3 (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g) |
|
A
|
67.2 L |
B
|
7.5 L |
C
|
22.4 L |
D
|
11.2 L |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Stoichiometry | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 58 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following gases would tend to be least ideal? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 59 |
Go |
Q:
|
If the pressure and the volume of a system both double, what has happened to the number of moles in the system if the temperature remains constant? |
|
A
|
the moles have doubled |
B
|
the moles have quadrupled |
C
|
the moles have halved |
D
|
the moles have not changed |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 60 |
Go |
Q:
|
What volume do the products of the reaction 4NH3 (g) + 5O2 (g) → 4NO (g) + 6H2O (g) occupy at STP if 4 moles of NH3 and 5 moles of O2 are present in the reaction? Assume the reaction goes to completion. |
|
A
|
10 L |
B
|
112 L |
C
|
224 L |
D
|
448 L |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 61 |
Go |
Q:
|
For the purposes of most chemical reactions, N2 is considered an inert gas and is used as a replacement atmosphere to prevent side reactions like oxidation. N2 is largely inert because: |
|
A
|
N2 is a noble gas |
B
|
N2 is cold and depresses the rate of side reactions |
C
|
N2 has a very strong triple bond |
D
|
N2 is much denser than air and forces out other reactive gas molecules |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 62 |
Go |
Q:
|
As the pressure on a gas increases without affecting its temperature, how is the ideality of the gas affected? |
|
A
|
The gas becomes more ideal due to the increase in density of the gas. |
B
|
The gas becomes more ideal due to the increase in pressure. |
C
|
The gas becomes less ideal due to the increase in density of the gas. |
D
|
The gas becomes less ideal due to the increase in pressure. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 63 |
Go |
Q:
|
A gas is held in a cylindrical chamber at a pressure P. If its temperature is held constant and the radius doubles, what is its new pressure? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 64 |
Go |
Q:
|
The ideal gas law states PV=nRT, where P is pressure, V volume, n moles, T temperature, and R the ideal gas constant. Which of the following are the correct units for R, the ideal gas constant? |
|
A
|
L·atm·mol-1·K-1 |
B
|
L·atm |
C
|
atm·mol·K |
D
|
atm·mol-1·K-1 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 65 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following increases the solubility of a gas in a liquid? |
|
A
|
Increasing temperature |
B
|
Decreasing pressure |
C
|
Decreasing temperature |
D
|
Increasing volume of the container |
|
|
|
Tags:
Fluids | Gases | |
|
| 66 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the volume that 11 grams of carbon dioxide occupies at STP? Assume that the gas constant, R = 0.1. |
|
A
|
3 L |
B
|
7 L |
C
|
10 L |
D
|
15 L |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 67 |
Go |
Q:
|
A thin test tube is filled with 10 mL of a volatile liquid. Its vapor pressure is measured. 10 mL of the substance is placed in a beaker with double the cross-sectional area. The vapor pressure is expected to: |
|
A
|
halve. |
B
|
double. |
C
|
quadruple. |
D
|
remain constant. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 68 |
Go |
Q:
|
A beaker of gas contains 24 moles of A, 36 of B, and 36 of C. What is the mole fraction of compound A? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 69 |
Go |
Q:
|
The Haber Process is a system which converts hydrogen and nitrogen gas into ammonia. What is coefficient of hydrogen gas in the stoichiometrically balanced equation for the Haber Process? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Stoichiometry | |
|
| 70 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following best explains why car tires are less inflated when the ambient temperature is lower? |
|
A
|
At constant pressure, the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to the temperature
|
B
|
The vapor pressure of the H2O decreases with decreasing temperature |
C
|
At constant volume, the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to temperature |
D
|
At constant volume, the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to temperature |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 71 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following noble gases listed will deviate the most from ideal behavior?
|
|
A
|
Helium |
B
|
Neon |
C
|
Krypton |
D
|
Xenon |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 72 |
Go |
Q:
|
A gas container with a movable piston inside currently shows that the piston is resting at the halfway mark in the container. If this piston were moved from the halfway mark all the way to the very top of the container, by what factor would the pressure change? |
|
A
|
Decrease by a factor of 2
|
B
|
Remains the same
|
C
|
Increase by a factor of 2
|
D
|
Increase by a factor of 4
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 73 |
Go |
Q:
|
A gas container with a movable piston inside currently shows that the piston is resting at the halfway mark in the container. If the number of moles of the gas in the container were doubled, how would the pressure and volume change? |
|
A
|
The pressure would decrease by a factor of 2, the volume would remain the same
|
B
|
The pressure would remain the same, the volume would decrease by a factor of 2
|
C
|
The pressure and volume would remain the same
|
D
|
The pressure would remain the same, the volume would increase by a factor of 2
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 74 |
Go |
Q:
|
The linear relationship of gas volume and temperature at constant pressure is independent of which of the following? |
|
A
|
Amount of gas, but not the type of gas |
B
|
Type of gas, but not the amount of gas |
C
|
Both amount and type of gas |
D
|
Neither amount of gas, nor the type of gas |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 75 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following best explains the relationship between pressure and volume when a balloon is squeezed? |
|
A
|
At constant temperature, the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the volume |
B
|
At constant temperature, the pressure of a gas is inversely proportional to the volume |
C
|
For an enclosed, elastic space, the relationship between pressure and volume depends on the gas being used |
D
|
At constant temperature, volume does not influence the pressure of the balloon |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 76 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following results in the doubling of the volume for an ideal gas? |
|
A
|
At constant pressure in a closed container, the temperature (in Kelvin) is doubled
|
B
|
At constant temperature in a closed container, the pressure is doubled
|
C
|
At constant pressure and temperature, two more moles of gas are added to a container that held 1 mole of gas
|
D
|
At constant pressure and temperature, the number of moles of the gas is quadrupled
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 77 |
Go |
Q:
|
The density of a gas in a closed container will increase if: |
|
A
|
The temperature of the gas increases under constant pressure
|
B
|
The pressure of the gas decreases under constant temperature |
C
|
The pressure of the gas increases under constant temperature
|
D
|
The number of moles of the gas decreases
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 78 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given a balloon containing N2, which of the following would double its volume? |
|
A
|
Reduce the temperature by a factor of 2
|
B
|
Reduce both the temperature and pressure by a factor of 2
|
C
|
Reduce the pressure by a factor of 2
|
D
|
Increase the pressure by a factor of 2
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 79 |
Go |
Q:
|
The main function of the respiratory system is to exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide. In humans, which of the following best describes how nearly all of the oxygen is carried in the blood? |
|
A
|
As gaseous O2
|
B
|
As erythroglobin
|
C
|
As hemoglobin
|
D
|
As bicarbonate
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Respiratory System | Gases | |
|
| 80 |
Go |
Q:
|
22.4L of a gas at standard temperature and pressure (STP) weighs 28 grams. Which of the following is NOT correct? |
|
A
|
This gas could be CO |
B
|
Even though the identity of this gas is not presented, the density of this gas at STP can be determined |
C
|
This gas could be a mixture of CO and N2 |
D
|
This gas could be 14 moles of H2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 81 |
Go |
Q:
|
Chatelier's principle is used to predict what happens to a chemical equilibrium upon a change in conditions. Which of the following is NOT an example of a reaction that correctly readjusts itself to a change in conditions? |
|
A
|
The amount of product increases if the concentration of a reactant increases. |
B
|
Given a reversible exothermic reaction that produces ammonia, less ammonia is produced if the temperature is increased. |
C
|
Given a reaction that produces ammonia, more ammonia is produced upon the addition of a catalyst. |
D
|
Given a reaction that changes from 2 total gas moles of reactants to 1 total gas mole of product, the equilibrium shifts to the reactant side if the volume is increased. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 82 |
Go |
Q:
|
The reaction below has a ΔH > 0 and an equilibrium pressure of 2 atm. Which of the following will shift the reaction to the left at equilibrium?
CO2 (g) → CO (g) + 1/2 O2 (g)
I. Increase volume
II. Decrease volume
III. Decrease temperature |
|
A
|
I only
|
B
|
II only
|
C
|
I and III only
|
D
|
II and III only
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Equilibrium | Gases | |
|
| 83 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following will increase the vapor pressure of a liquid? |
|
A
|
Decreasing the temperature of the liquid
|
B
|
Increasing the temperature of the liquid
|
C
|
Decreasing the surface area of the liquid
|
D
|
Increasing the surface area of the liquid
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Fluids | Molecular Bonding | |
|
| 84 |
Go |
Q:
|
In an experiment, a radioactive metal atom experiences alpha decay and the alpha particles are collected as a gas. If the gas volume collected contains 2 x 10-6 moles, how many total atoms decayed? |
|
A
|
12 x 1018 atoms
|
B
|
6 x 1020 atoms
|
C
|
1.2 x 1019 atoms
|
D
|
1.2 x 1018 atoms
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Quantitative Skills | Nuclear Chemistry | Gases | |
|
| 85 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is true regarding the solubility of a gas? |
|
A
|
As temperature increases, the solubility of a gas increases.
|
B
|
As temperature decreases, the solubility of a gas decreases.
|
C
|
As pressure increases, the solubility of a gas decreases.
|
D
|
As pressure decreases, the solubility of a gas decreases.
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Gases | |
|
| 86 |
Go |
Q:
|
An object is placed on a scale and its weight is recorded. How would the recorded weight of the object change as the atmospheric pressure was increased? |
|
A
|
The recorded weight would increase because the air density increases as pressure increases. |
B
|
The recorded weight would increase because air density decreases as pressure increases. |
C
|
The recorded weight would decrease because the air density increases as pressure increases. |
D
|
The recorded weight would decrease because the air density decreases as pressure increases. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Fluids | Forces | |
|
| 87 |
Go |
Q:
|
Carbonation of an aqueous solution can be increased by: |
|
A
|
decreasing the pressure on the solution. |
B
|
decreasing the temperature of the solution. |
C
|
adding carbonic anhydrase. |
D
|
decreasing the surface area of the solution. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Solutions | Gases | |
|
| 88 |
Go |
Q:
|
A 45 L CO2 tank has a pressure of 50 atm at 0 °C. What is the approximate mass of the CO2 in the tank assuming it is an ideal gas? |
|
A
|
2.5 kg |
B
|
4.4 kg
|
C
|
9 kg |
D
|
12 kg |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 89 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is a true statement regarding ideal gases? |
|
A
|
The volume of an ideal gas is less than the volume of the equivalent real gas. |
B
|
The pressure of an ideal gas is less than the volume of the equivalent real gas. |
C
|
The size of molecules is included in calculations involving ideal gases. |
D
|
The relationship where increased volume results in decreased pressure is only true for ideal gases. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 90 |
Go |
Q:
|
At approximately what temperature will 1 mole of argon gas occupy 10 liters of volume at 100 atm of pressure? |
|
A
|
2000 K |
B
|
6000 K |
C
|
10000 K |
D
|
12000 K |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 91 |
Go |
Q:
|
The transition of a solid to the gas phase is called: |
|
A
|
vaporization. |
B
|
sublimation. |
C
|
freezing. |
D
|
condensation. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 92 |
Go |
Q:
|
A container at standard atmospheric pressure contains two gases, A and B. It contains 1/3 moles of gas A and 5/3 moles of gas B. Which of the following is the approximate partial pressure of gas A in the container? |
|
A
|
0.1 atm |
B
|
0.16 atm |
C
|
0.2 atm |
D
|
0.3 atm |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 93 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is NOT an assumption made in the ideal gas law as it pertains to kinetic molecular theory? |
|
A
|
molecules within gases have negligible volume |
B
|
collisions between two gas molecules is inelastic |
C
|
gas particles move randomly with respect to each other |
D
|
there are no attractive or repulsive forces between molecules |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 94 |
Go |
Q:
|
A chamber contains a gas of pressure X at a temperature of 127 degrees Celcius. In order to double the pressure on the gas, temperature must be increased by: |
|
A
|
127 degrees Celcius. |
B
|
63 degrees Celcius. |
C
|
400 Kelvin. |
D
|
200 Kelvin. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 95 |
Go |
Q:
|
A specific gas is dissolved in a volume Y of solution to achieve a molarity of X at a pressure Z. Which of the following depicts the concentration of the gas under a pressure P? |
|
A
|
(Z*Y)/(X*P) |
B
|
Z/P |
C
|
(X*P)/(Z*Y) |
D
|
(X*P)/Z |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 96 |
Go |
Q:
|
Gas A has a molar mass four times the mass of gas B. The rate of diffusion of gas A will be: |
|
A
|
one-quarter that of gas B. |
B
|
half that of gas B. |
C
|
the same as that of gas B. |
D
|
double that of gas B. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 97 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is not an assumption made for the ideal gas law? |
|
A
|
The gas is under standard temperature and pressure settings. |
B
|
Volume is negligible for the gas. |
C
|
The density of each gas molecule is not very large. |
D
|
Intermolecular interactions are minimal between the gas particles. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 98 |
Go |
Q:
|
AT standard temperature and pressure, approximately 110g of a gas is noted to occupy about 90L of space. Which of the following is the gas? |
|
A
|
propane |
B
|
CO |
C
|
C3H6 |
D
|
Br2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 99 |
Go |
Q:
|
Gas A diffuses effuses through a hole at a rate R. If gas B is quadruple the mass of gas A, how fast will gas B diffuse through the hole? |
|
A
|
R/4 |
B
|
R/2 |
C
|
R/sqrt(2) |
D
|
R |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 100 |
Go |
Q:
|
Assuming that all of the following gases exist as diatomic molecules, which of the following noble gases would be expected to function least as an ideal gas? |
|
A
|
krypton |
B
|
xenon |
C
|
helium |
D
|
neon |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 101 |
Go |
Q:
|
A fixed volume chamber is filled with some amount of a non-volatile ideal gas. Pressure is increased in a linear fashion. What kind of curve would the temperature change be expected to follow? |
|
A
|
linear increase |
B
|
linear decrease |
C
|
exponential increase |
D
|
exponential decrease |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 102 |
Go |
Q:
|
How many moles of a diatomic gas at STP would be required to occupy 200L of volume? |
|
A
|
4.5 moles |
B
|
9 moles |
C
|
20 moles |
D
|
40 moles |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 103 |
Go |
Q:
|
Gas A is noted to diffuse at triple the rate of a second gas, gas B. This implies that: |
|
A
|
Gas A has triple the mass of gas B. |
B
|
Gas B has greater than triple the mass of gas A. |
C
|
Gas A is more dense than gas B. |
D
|
Gas B has a lower condensation point than gas A. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 104 |
Go |
Q:
|
The van der Waals equation suggests the relationship that: |
|
A
|
the larger the volume of a gas molecule, the less the gas follows the ideal gas law. |
B
|
the faster a molecule is traveling, the higher its temperature. |
C
|
all compounds have a triple point, i.e. a temperature-pressure combination where solid, liquid, and gas phases all exist |
D
|
magnetic fields run in perpendicular to electric fields. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 105 |
Go |
Q:
|
A spherical container with a volume of 30 L contains 320g of methane and 300g of ethane. What is the total pressure in the sphere assuming the temperature in the sphere is 27 degrees celcius? |
|
A
|
4 atm |
B
|
8 atm |
C
|
12 atm |
D
|
24 atm |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 106 |
Go |
Q:
|
van der Waals equation suggests that: |
|
A
|
gas molecules become more ideal as the size of the molecule increases in size |
B
|
intermolecular forces are not important for determining deviation of gases from ideal state |
C
|
as temperature increases as does the volume of a gas |
D
|
intra-atomic forces are not important for determining deviation of gases from ideal state |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 107 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is false regarding phase diagrams? |
|
A
|
three phases exist at the triple point |
B
|
they display the relationship of pressure and temperature for a compound |
C
|
at sufficiently high pressure and temperature, all substances will exist in the gas phase |
D
|
solid and gas do not exist in equilibria with each other |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 108 |
Go |
Q:
|
A liquid substance of molecular mass 25 g/mol is found to have a density of 10 g/mL. If one mole of this compound is evaporated at STP, how much approximate volume increase would be expected to take place for this compound? |
|
A
|
5000-fold increase |
B
|
10000-fold increase |
C
|
15000-fold increase |
D
|
20000-fold increase |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
| 109 |
Go |
Q:
|
In an ideal gas where the temperature and number of moles of a gas remain constant, as pressure increases: |
|
A
|
the number of atoms of gas decreases. |
B
|
the volume of the gas decreases. |
C
|
the density of the gas decreases. |
D
|
the average kinetic energy of the gas decreases. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | |
|
|
Questions? We're here to help!
Ask Us
|