|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular enzyme-substrate complex is under investigation. A certain molecule is noted to have inhibitory effects on the uptake of substrate by the enzyme. Under further testing, it is noted that the shape of the enzyme without the inhibitor is slightly pentagonal, while with the inhibitor, the enzyme is cuboidal. This inhibitor is likely a(n) |
|
A
|
Irreversible inhibitor |
B
|
Competitive inhibitor |
C
|
Noncompetitive inhibitor |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
In superoxide dismutase 1, an enzyme implicated in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, a copper ion is bound to the active site and is important for enzyme activity. In this enzyme, copper most likely functions as a(n) |
|
A
|
coenzyme |
B
|
cofactor |
C
|
allosteric activator |
D
|
allosteric inhibitor |
|
|
|
Tags:
Enzyme Structure and Function | Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
An overall reaction is made up of 20 elementary reactions. Halfway through the reaction mechanism, the concentration of one particular species has decreased. What is the most likely role of this species in the reaction? |
|
A
|
Reactant |
B
|
Catalyst |
C
|
Intermediate |
D
|
A and B |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
Examination of a patient shows a deficiency in enzyme activity due to a particular dietary deficiency of a partiular micronutrient metal. Which of the following options provides the most likely function of the metal?
|
|
A
|
cofactor |
B
|
reactant |
C
|
energy source |
D
|
chelating agent |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
Dr. Frankenstein notices that his creation has an unusual genetic disorder which results in a change in one amino acid residue on pepsin. This mutated pepsin has optimal activity at a pH of 4. What effect is expected on the creation? |
|
A
|
Neurons will decrease firing speed |
B
|
There will be a noticeable increase of oxygen in tissue |
C
|
Digestion will be severely suppressed |
D
|
No muscle contraction due to an absence in the release of Ca2+. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | Digestive System | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
A new inducer-receptor interaction shows that the inducer activates the transcription of certain genes only once a high-concentration threshold of inducer concentration is reached. The presence of a high concentration threshold implies what about the mechanism of inducer-receptor interaction? |
|
A
|
strong binding interaction |
B
|
weak binding interaction |
C
|
negative feedback loop |
D
|
inhibition of the receptor |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
In a particular synapse, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor is administered. Which of the following impacts will be seen on the neuronal network? |
|
A
|
Decreased production of acetylcholine |
B
|
Decrease in neuronal stimulation |
C
|
Increased rate of fatigue in the pre-synaptic neuron |
D
|
Continuous stimulation of the post-synaptic neuron |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | Nervous System | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
The hormone glucagon binds to a G protein-coupled receptor to activate a cellular response. If a competitive inhibitor to the receptor is present, what is the overall effect in the body? |
|
A
|
Blood sugar decreases |
B
|
Blood sugar increases |
C
|
Decreased glucagon in the pancreas |
D
|
Increased osmotic pressure of the blood. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | Hormonal Regulation | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
A non-competitive inhibitor binds to an allosteric site and prevents substrate from binding to the active site. Non-competitive inhibition |
|
A
|
is affected by concentrations of substrate |
B
|
increases Vmax of a reaction |
C
|
maintains constant Vmax of a reaction |
D
|
cannot be overcome by increasing substrate concentration |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
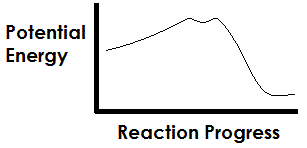
The graph above depicts a typical curve of a catalyzed reaction, with the spike in potential energy representing the activation energy of the reaction. In terms of the structure of the compounds involved in the reaction, what does the small dip in the potential energy curve represent? |
|
A
|
The accumulation of electrons in an unfavorable state |
B
|
The intermediate compound |
C
|
The reactant |
D
|
The product |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following will not change the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction? |
|
A
|
increasing the substrate concentration beyond the saturation point |
B
|
decreasing the temperature |
C
|
changing the pH |
D
|
removal of a competitive inhibitor |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is false about a catalyst? |
|
A
|
A catalyst is altered during the course of a reaction and resumes its original state after the completion of a reaction. |
B
|
The maximum reaction rate increases with the addition of more catalyst. |
C
|
The rate constant, k, of a reaction rate law remains unchanged in the presence of catalyst. |
D
|
The rate of a catalyzed reaction decreases over time if substrate is not continually supplied. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Enzyme Structure and Function | Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is not activated by trypsin? |
|
A
|
chymotrypsin |
B
|
lipase |
C
|
pancreatic amylase |
D
|
pepsin |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TDT) is an enzyme that does not require a template and can essentially add a random sequence of nucleotides to a DNA strand. B and T lymphocytes express the enzyme during development as a mechanism for having each cell produce a unique antigen receptor protein. Certain lymphocytes, however, lack TDT. Such lymphocytes would be expected to |
|
A
|
have limited diversity of their antigen receptors. |
B
|
employ DNA Polymerase III to generate diverse antigen receptors. |
C
|
be especially susceptible to attack by foreign antigens. |
D
|
be more short-lived in the blood due to stunted growth. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | Immune System | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
Hemoglobin has far more affinity for carbon monoxide than for oxygen at its binding site. When carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin, the bond is noncovalent. Which of the following accurately describes the type of inhibition exhibited by carbon monoxide on hemoglobin? |
|
A
|
competitive inhibition |
B
|
noncompetitive inhibition |
C
|
allosteric inhibition |
D
|
irreversible inhibition |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | Circulatory System | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
The pancreas is responsible for the release of a significant amount of digestive enzymes which assist in the absorption of nutrients from food. The pancreas often stores these enzymes in their nonactive, zymogen form. When the enzymes are pumped into the small intestine, they can be activated through cleaving enzymes. Which of the following correctly explains why these enzymes would be released in a zymogenic form? |
|
A
|
To prevent pancreatic damage |
B
|
To ensure that activation occurs prior to food entry into the duodenum |
C
|
To prevent the retrograde flow of enzymes from the small intestine to the pancreas |
D
|
To increase the catalytic rate of the digestive enzymes |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | Digestive System | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
Sildenafil (viagra) is a common treatment for male erectile dysfunction. It acts through inhibition of PDE5 (phosphodiesterase type 5) in order to prevent the degradation of a cGMP (the substrate for PDE5). This, in turn, allows for smooth muscle relaxation and erection in the penis. The inhibition dynamics of sildenafil are examined through measuring the catalytic rate of PDE5 in the presence of the drug. It is found that doubling cGMP concentration has almost no effect on the catalytic rate. Which of the following is possible for sildenafil? |
|
A
|
PDE5 inhibition by sildenafil can be saturated and diminished with enough addition of cGMP |
B
|
Decreasing cGMP concentrations will decrease the catalytic rate of the reaction |
C
|
Decreased cGMP levels will result in an increase in catalytic rate |
D
|
Sildenafil is a noncompetitive inhibitor |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
A researcher develops an enzyme inhibitor by creating an analog that is very similar to the substrate of the enzyme. However, she finds that the inhibitor lacks some important similarities to the substrate and although the structures are substantially similar, the inhibitor does not bind to the enzyme. This observation suggests what about the nature of how the enzyme binds to its substrate? |
|
A
|
The substrate forms covalent bonds to its enzyme |
B
|
The inhibitor binds allosterically to the enzyme |
C
|
The enzyme binds to its substrate using the induced fit model |
D
|
The enzyme has very low affinity for its substrate |
|
|
|
Tags:
Enzyme Structure and Function | Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
Naloxone is a drug given to individuals who present in the emergency room suspected of opiate overdose (such as heroin). Naloxone acts on neurons which have opiate receptors to block the binding of the opiates in the body, thus negating their toxic effects. The drug acts quite quickly such that patients will suddenly wake up from unconsciousness upon administration. Naloxone has a halflife of around 30 minues (as compared with 4 hours for many opiates). As such, the patient may revert into the unconscious state when the naloxone effects have worn off and the opiates continue to have their effects. Which of the following types of inhibition is POSSIBLE of the naloxone-opiate receptor system?
I. Noncompetitive inhibitor
II. Competitive inhibitor
III. Suicide Inhibitor |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
II only |
C
|
II and III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 20 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is true regarding noncompetitive inhibition? |
|
A
|
The enzyme is prevented from binding to the substrate. |
B
|
The inhibitor binds to the same site as the substrate. |
C
|
The substrate and inhibitor can bind to the enzyme simultaneously. |
D
|
The inhibitor binds to the substrate directly. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
Carbon monoxide binds to hemoglobin in the same location where oxygen binds. This suggests that carbon monoxide acts as which type of molecule? |
|
A
|
Noncompetitive inhibitor |
B
|
Allosteric inhibitor |
C
|
Uncompetitive inhibitor |
D
|
Competitive inhibitor |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
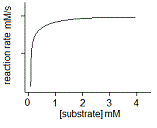
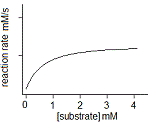
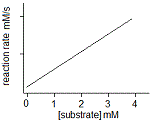
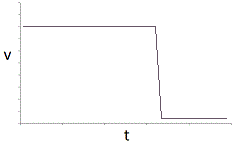
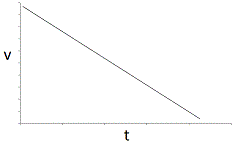
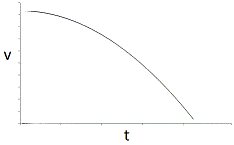
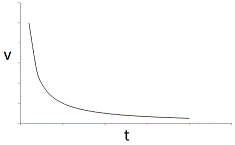
In an experiment, a student varies the substrate concentration of an enzymatic reaction and measures the corresponding reaction rate, yielding the graph below. The student then adds a noncompetitive inhibitor to the enzyme and repeats the experiment. Which of the following graphs accurately depicts the new relationship between reaction rate and substrate concentration in the presence of the noncompetitive inhibitor?
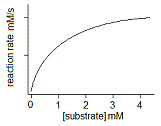 |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 23 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is FALSE regarding enzymes? |
|
A
|
Decreasing the substrate decreases the reaction rate. |
B
|
Removal of an enzyme cofactor reduces the ability of the enzyme to catalyze the reaction. |
C
|
The presence of a competitive inhibitor will not affect the vmax of the reaction. |
D
|
An increase in the substrate concentration will increase the value of vmax. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 24 |
Go |
Q:
|
An inhibitor is found to bind to an enzyme whether the substrate is bound or not, but has a strong preference for the enzyme when it is bound to the substrate. This is an example of: |
|
A
|
competitive inhibition |
B
|
mixed inhibition |
C
|
noncompetitive inhibition |
D
|
uncompetitive inhibition |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 25 |
Go |
Q:
|
For a drug that binds and inhibits its protein target irreversibly, which of the following would be expected? |
|
A
|
The effects of the drug last only as long as the patient is actively consuming the drug. |
B
|
The effects of the drug last for several days or longer after the patient stops taking the drug. |
C
|
The drug permanently disables the function in question and the patient no longer needs to take the drug. |
D
|
The patient becomes dependent on the drug and must not stop taking it to prevent reversal of the target activity. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Enzyme Structure and Function | Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 26 |
Go |
Q:
|
In uncompetitive inhibition, the inhibitor binds only to the enzyme-substrate complex and prevents the catalysis from occurring. Given this information, for which of the following substrate concentrations would an uncompetitive inhibitor be expected to work most effectively? |
|
A
|
1 μM |
B
|
1.5 μM |
C
|
5 μM |
D
|
15 μM |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 28 |
Go |
Q:
|
Compared to an uncatalyzed reaction, which of the following is NOT true regarding the same reaction now with a catalyst? |
|
A
|
The catalyzed reaction will release more energy
|
B
|
The catalyzed reaction will occur faster
|
C
|
The catalyzed reaction will have a lower activation energy
|
D
|
The catalyzed reaction will proceed and not consume any of the catalyst
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 29 |
Go |
Q:
|
Protease (an HIV enzyme) contains hydrophobic residues at its active site. Which of the following would be an ideal characteristic for a drug that would act as a competitive inhibitor to protease? The drug should be: |
|
A
|
Polar |
B
|
Nonpolar |
C
|
Charged |
D
|
Neutral |
|
|
|
Tags:
Enzyme Structure and Function | Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 30 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is a true statement regarding cofactors and coenzymes? |
|
A
|
Cofactors and coenzymes allow enzymes to catalyze a wider range of chemical reactions
|
B
|
Cofactors and coenzymes allow enzymes to function at lower concentrations
|
C
|
Cofactors and coenzymes maximize the ΔG
|
D
|
Cofactors and coenzymes change endergonic reactions to exergonic reactions
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Enzyme Structure and Function | Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 31 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is a correct statement regarding a competitive inhibitor of an enzyme? |
|
A
|
The competitive inhibitor changes the enzyme shape by binding to a site other than the active site
|
B
|
The competitive inhibitor binds to the product of the enzymatic reaction
|
C
|
The competitive inhibitor, which resembles the shape of the substrate, binds to the active site
|
D
|
The competitive inhibitor causes the enzyme reaction to become nonspontaneous
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Enzyme Structure and Function | Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 32 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is NOT correct regarding the control and regulation of gluconeogenesis? |
|
A
|
The control of gluconeogenesis is inversely linked to the control of glycolysis
|
B
|
Glucagon stimulates adenylyl cyclase, which causes cAMP formation
|
C
|
Most of the enzymes responsible for the control and regulation of gluconeogenesis are found in the cytoplasm
|
D
|
Acetyl-CoA only activates gluconeogenesis enzymes and has no inhibitory role in gluconeogenesis
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Enzyme Structure and Function | Glycolysis, Gluconeogenesis, PPP | Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 33 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is TRUE regarding a competitive inhibitor? |
|
A
|
A competitive inhibitor binds reversibly at the enzyme's active site. |
B
|
A competitive inhibitor covalently binds to the enzyme. |
C
|
A competitive inhibitor decreases the maximum velocity of the reaction. |
D
|
A competitive inhibitor binds at multiple different sites on the enzyme. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Enzyme Structure and Function | Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 35 |
Go |
Q:
|
An increase in the KM of a protein could be a result of: |
|
A
|
negative regulation, because the protein's affinity for its substrate decreases.
|
B
|
positive regulation, because the protein's affinity for its substrate decreases. |
C
|
negative regulation, because the protein's affinity for its substrate increases. |
D
|
positive regulation, because the protein's affinity for its substrate increases. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | Enzyme Structure and Function | |
|
| 36 |
Go |
Q:
|
The a key enzyme for the production of tetradecanoic acid has an allosteric binding site for tetradecanoic acid. The purpose of the binding site is most likely: |
|
A
|
positive feedback |
B
|
cooperative binding |
C
|
feedback inhibition |
D
|
zymogen activation |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 37 |
Go |
Q:
|
An enzyme with a low KM will: |
|
A
|
denature at a higher temperature than an enzyme with a high KM. |
B
|
reach its vmax at a lower substrate concentration than an enzyme with a high KM. |
C
|
have fewer allosteric inhibitor sites than an enzyme with a high KM. |
D
|
have a higher vmax than an enzyme with a high KM. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Enzyme Structure and Function | Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
| 38 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which type of inhibition does NOT affect the Km of the reaction? |
|
A
|
noncompetitive |
B
|
competitive |
C
|
uncompetitive |
D
|
mixed |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | |
|
|
Questions? We're here to help!
Ask Us
|