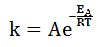|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
The following reaction has a negative change in enthalpy: 2NO(g)+O2(g) <-->2NO2(g). Which of the following would increase the ratio of NO2 to NO at equilibrium? |
|
A
|
Decreasing the volume of the system. |
B
|
Inserting a catalyst. |
C
|
Removing oxygen from the system. |
D
|
Increasing the temperature. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is a spontaneous process? |
|
A
|
A process where the change in entropy of the system is positive. |
B
|
Two gases in one container maintaining different temperatures. |
C
|
The precipitation of sodium chloride when 1 mole of NaCl is added 2L of water. |
D
|
None of the above. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
A first order reaction has a rate constant of k = 0.7 x 10-3. At what time would you have
1/8 of your original concentration of reactant? |
|
A
|
8 x 0.7 x 10-3 s |
B
|
3 x 103 s |
C
|
3 x 10-3 s |
D
|
8 x 0.7 x 103 s |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular reaction can be simplified to the following form: A -> B + Heat (i.e. an exothermic reaction). Assume that the reaction occurs in a closed environment. Say that the forward rate of the reaction is k1 and the reverse rate of the reaction is k-1. If temperature of the system was decreased, what would be the expected effect on k1 and k-1? |
|
A
|
k1 increases, k-1 decreases |
B
|
k1 decreases, k-1 increases |
C
|
Both k1 and k-1 decrease |
D
|
k1 and k-1 remain constant. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following rate laws is most likely to have the rate constant with the largest magnitude, assuming that all the associated reactions are elementary? |
|
A
|
k[H2][O2] |
B
|
k[Fe]4[O2]3 |
C
|
k[H2]2[O2] |
D
|
k[Cl2][Na]2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
What are the units on the rate constant of a third order reaction? |
|
A
|
L-1s1mol1 |
B
|
Ls-1mol-1 |
C
|
L3s-1mol-3 |
D
|
L2s-1mol-2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
A zero order reaction is as follows: A + B + C -> D. There are three intermediate steps in forming D from A,B, and C. If the concentration of A and B both increase, how will the rate of the reaction change assuming constant pressure and temperature? |
|
A
|
Remain the same |
B
|
Double |
C
|
Quadruple |
D
|
Half |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following statements best describes the relationship between the energy in GTP and ATP? |
|
A
|
GTP has significantly more energy than ATP |
B
|
ATP has significantly more energy than GTP |
C
|
The two are interchangeable in terms of energy |
D
|
The two have substantially different metrics of energy which cannot be compared to one another |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
A gas decomposes via zero order reaction to twice the number of moles. If the first half-life of the reaction is complete in 20 seconds, and the volume of the reaction system is 1 L, what will the volume be after 40 seconds? Assume constant temperature and pressure. |
|
A
|
1.5 L |
B
|
1.75 L |
C
|
2 L |
D
|
The volume cannot be determined from the information given. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Gases | Chemical Kinetics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
A first-order reaction has a half-life of 10 hours. How long will it take for the substance to decay to 6% of its initial value? |
|
A
|
10 hours |
B
|
20 hours |
C
|
40 hours |
D
|
80 hours |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
What does the speed of an SN1 reaction depend on? |
|
A
|
The concentration of substrate only |
B
|
The concentration of the nucleophile only |
C
|
The concentration of both the substrate and the nucleophile |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
A zero order reaction is as follows: A + B + C → D. There are three intermediate steps in forming D from A,B, and C. If the concentration of A and B both increase, how will the rate of the reaction change assuming constant pressure and temperature?
|
|
A
|
Remain the same |
B
|
Double |
C
|
Quadruple |
D
|
Half |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
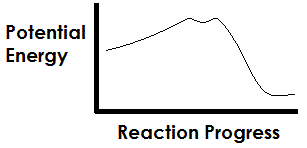
The graph above depicts a typical curve of a catalyzed reaction, with the spike in potential energy representing the activation energy of the reaction. In terms of the structure of the compounds involved in the reaction, what does the small dip in the potential energy curve represent? |
|
A
|
The accumulation of electrons in an unfavorable state |
B
|
The intermediate compound |
C
|
The reactant |
D
|
The product |
|
|
|
Tags:
Control of Enzyme Activity | Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the rate law for the given reactions:
NO2 + NO2 → NO3 + NO (slow reaction)
NO3 + CO → NO2 + CO2 (fast reaction)
|
|
A
|
k[NO3][NO] |
B
|
k[NO3][CO] |
C
|
k[NO2]2 |
D
|
k[NO2][CO2] |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
The following elementary reaction was performed:
NO + O3 ↔ NO2 + O2.
Which of the following correctly describes the rate equation? kf represents for the forward rate, while kr is for the reverse reaction. |
|
A
|
Rate = kf[NO]2[O3] |
B
|
Rate = kr[NO2][O2] |
C
|
Rate = kf[NO][O3][NO2][O2] |
D
|
Rate = kr[NO][O3] |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
You are given the following reaction:
A + 2B → C
Three experiments were done to determine the rate law for this reaction. The following results were obtained:
Trial 1: [A] = 0.1, [B] = 0.05, Initial Rate = 1 x 10-4
Trial 2: [A] = 0.1, [B] = 0.1, Initial Rate = 2 x 10-4
Trial 3: [A] = 0.2, [B] = 0.1, Initial Rate = 5 x 10-5
What is the rate law for this reaction?
|
|
A
|
Rate = [A][B]
|
B
|
Rate = [A]2[B]
|
C
|
Rate = [A][B]2
|
D
|
Rate = [A]-2[B] |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
The rate of the non-elementary reaction below is measured at three differing concentrations of reactants as in the given table. What is the order of the reaction?
A + B → C + D
| Experiment | [A] | [B] | Initial Rate
(mol/L*s) |
| 1 | 0.01 M | 0.005 M | 1.56 x 10-3 |
| 2 | 0.01 M | 0.050 M | 1.49 x 10-1 |
| 3 | 0.10 M | 0.005 M | 1.62 x 10-3 |
|
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
A reaction is given by the following equation:
3 A + B → 2 C + D
Over 5 seconds, the concentration of reactant A decreased from 8.0 x 10-5 M to 2.0 x 10-5 M. What is the rate of the reaction?
|
|
A
|
6 x 10-5 M/s |
B
|
4 x 10-6 M/s |
C
|
2 x 10-5 M/s |
D
|
1.2 x 10-6 M/s |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the Ksp of the following compound when dissolved in water
AB2 → A+ + 2B-
if the concentrations of A and B are 0.2 M and 0.4 M, respectively? |
|
A
|
0.032 M3 |
B
|
0.080 M3 |
C
|
0.320 M3 |
D
|
2.000 M3 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 20 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular enzyme-catalyzed biological reaction (Reaction 1) in humans takes the substrate A and converts it to B. The ΔG is -100 kJ/mol. A different enzyme is later found which also has A as a substrate (Reaction 2). The identity of the product from this different enzyme is not recorded. It is found that the ΔG for this new reaction is -120 kJ/mol. Which of the following holds true? |
|
A
|
Reaction 2 must run faster kinetically than Reaction 1 |
B
|
The second enzyme is more efficient at converting A to B due to the larger decrease in free energy |
C
|
Reactant A can bind to 2 enzymes at a time |
D
|
The product of Reaction 2 cannot be B |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
The reaction CaCO3 → CaO + CO2 proceeds through two intermediate, unknown steps. What is the rate law for this reaction? |
|
A
|
k[CaCO3] |
B
|
k[CaCO][CO2] |
C
|
k |
D
|
Cannot be determined from the given information. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
First order reactions are important in chemical reactions as well as in pharmacology. First order refers to the rate of a reaction. If the reaction is A-->B, then stating that it is first order implies that rate=k*[A], where k is some constant and [A] is the concentration of A. Which of the following does not hold true for such an order reaction? |
|
A
|
The slope of log([A]) over time is linear |
B
|
Half-life depends on the concentration of A |
C
|
If [A] doubles, so will the rate of the reaction |
D
|
Changing [B] will have no impact on the rate |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 23 |
Go |
Q:
|
As the concentration of the products of a reversible reaction increase, which of the following will be affected? |
|
A
|
Activation Energy |
B
|
Equilibrium constant of the reaction |
C
|
Order of the reaction |
D
|
Rate of the forward reaction |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 24 |
Go |
Q:
|
Under which of the following conditions would the reaction
Rate = k[A]x[B]y
be considered a third order reaction? |
|
A
|
x = 1 and y = 2 |
B
|
x = 3 and y = 3 |
C
|
x = 3 and y ≠ 0 OR y = 3 and x ≠ 0 |
D
|
x - y = 0 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 25 |
Go |
Q:
|
The kcat is a measurement of the number of molecules of product that an enzyme can produce per second. Highly efficient enzymes have kcat values upwards of 108 s-1. If a solution containing an enzyme with a kcat of 105 s-1 is able to produce 0.001 M of product per second, what is the concentration of the enzyme? |
|
A
|
1 x 10-6 M |
B
|
6 x 10-5 M |
C
|
1 x 10-8 M |
D
|
6 x 10-3 M |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 26 |
Go |
Q:
|
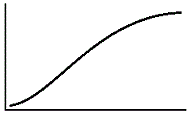
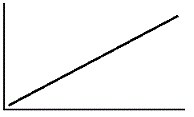
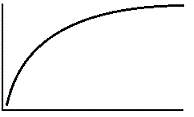
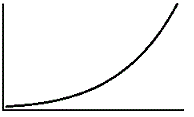
An enzyme solution is added to a solution of substrate and the concentration of product is measured from t = 0. Which of the following graphs accurately depicts the graph of the product concentration versus time? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Enzyme Structure and Function | Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 27 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following always holds true about a second order rate reaction? |
|
A
|
It usually depends on the concentration of one reactant reacting with itself |
B
|
It usually depends on the concentrations of two different reactions |
C
|
Half-life remains constant despite changes in reactant concentrations |
D
|
The sum of all exponents in the rate law equation is 2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 28 |
Go |
Q:
|
Reactions A and B are unrelated and each has its equilibrium constant measured. Reaction A has K = 4 x 102 and Reaction B as K = 2.8 x 10-1. Which of the following statements must hold true given this information? |
|
A
|
The forward reaction rate of A is greater than the forward reaction rate of B. |
B
|
The forward reaction rate of B is greater than the forward reaction rate of A. |
C
|
The reverse reaction rate of A is greater than the forward reaction rate of B. |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | Chemical Equilibrium | |
|
| 29 |
Go |
Q:
|
The steps of the net enzymatic reaction Substrate (S) ↔ Product (P) can be written as follows, where E represents the enzyme:
E + S ↔ ES ↔ EP ↔ E + P
In most enzymatic reactions, the rate-limiting step is the binding of the substrate to the enzyme. This suggests the rate law of the overall reaction S ↔ P can be written as: |
|
A
|
rate = k[E][S] |
B
|
rate = k[ES] |
C
|
rate = k[E][P] |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined from the given information. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 30 |
Go |
Q:
|
In a container a solid called X will spontaneously become solid Y and gas Z (1 molecule of X becomes 1 molecule of Y and 1 molecule of Z). Which of the following correctly depicts the equilibrium expression of the reaction? |
|
A
|
K = [X]/[Y][Z] |
B
|
K = [Y][Z]/[X] |
C
|
K = [Y][Z] |
D
|
K = [Z] |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 31 |
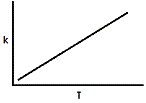
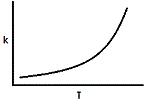
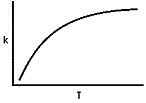
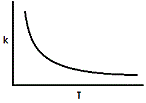
Go |
Q:
|
The Arrhenius equation describes the relationship of the reaction rate constant k to the reaction activation energy and temperature. The equation is given by:
k = Ae-Ea/(RT)
Where A and R are constants in a reaction and Ea is the activation energy. Assuming the activation energy is held constant, which of the following graphs accurately describes the relationship of the rate constant and temperature? |
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 32 |
Go |
Q:
|
For a reaction whose rate law is Rate = k[A][B]2, the rate of the reaction is 0.250 M/s when the concentration of B is 0.1 M. What is the rate of the reaction if the concentration of B is 0.2 M, all else being equal? |
|
A
|
0.250 M/s |
B
|
0.500 M/s |
C
|
1.000 M/s |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined with the given information. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 33 |
Go |
Q:
|
The following data were collected for the reaction A + B → C.
| Exp | [A] (M) | [B] (M) | Initial Rxn Rate (M/s) |
| 1 |
0.20 |
0.10 |
4 x 10-4 |
| 2 |
0.10 |
0.20 |
4 x 10-4 |
| 3 |
0.20 |
0.20 |
8 x 10-4 |
What is the rate law for this reaction?
|
|
A
|
Rate = k[A][B] |
B
|
Rate = k[A]2[B] |
C
|
Rate = k[A][B]2 |
D
|
Rate = k[A]2[B]2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 34 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following rate law equations depicts a third order reaction? |
|
A
|
rate = k[A][B] |
B
|
rate = k[A]3[B] |
C
|
rate = k[A]2[B] |
D
|
rate = k[A]3[B]3 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 35 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the rate law for the following reaction? The reaction may proceed through one or more steps.
2NO + 2H2 → N2 + 2H2O |
|
A
|
k[NO]2[H2]2 |
B
|
k[N2][H2]2 |
C
|
k([N2][H2]2/[NO]2[H2]2) |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined with the information given. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 36 |
Go |
Q:
|
Reaction 1: A → B + C
Reaction 2: 2B + D → E
A scientist is determining the order of a reaction. The reaction is composed of two elementary reactions as shown above. If Reaction 1 is slower than Reaction 2, what is the order of the overall reaction? |
|
A
|
0 |
B
|
1 |
C
|
2 |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined with the given information |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 37 |
Go |
Q:
|
The product of the zero order reaction X + Y → Z will |
|
A
|
increase linearly |
B
|
decrease linearly |
C
|
increase exponentially |
D
|
decrease exponentially |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 38 |
Go |
Q:
|
The Arrhenius equation, shown below, is a description of the relationship between the rate constant, k, the activation energy of the reaction, and the temperature in Kelvin.
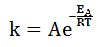
Here, A and R are constants. For ratios of EA/RT that are greater than 1, if the constant R were half of its actual value, what would happen to the rate constant k? |
|
A
|
It would increase by less than double. |
B
|
It would increase by more than double. |
C
|
It would decrease to less than half of its current value. |
D
|
It would decrease to more than half of its current value. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Thermochemistry | Chemical Kinetics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 39 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following rate laws depicts a second order reaction? |
|
A
|
k[A]2[B] |
B
|
k[A][B]2 |
C
|
k[A]2[B]2 |
D
|
k[A][B] |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 40 |
Go |
Q:
|
2 CH4 + 3 Cl2 → 2 CH3Cl + 2 HCl + 2 Cl-
The reaction above proceeds through the following two steps:
1. 2 CH4 + Cl2 → 2 CH3+ + 2 HCl
2. CH3+ + Cl2 → CH3Cl + Cl-
If the first of the two steps is the slow step, the rate equation of the overall reaction can be written as which of the following? |
|
A
|
k[CH4]2[Cl2]3 |
B
|
k[CH4]2[Cl2] |
C
|
k[CH3+][Cl2] |
D
|
k[CH3+][CH4]2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 41 |
Go |
Q:
|
A reaction is studied in a reaction chamber. The stoichiometrically balanced reaction is as follows: aX + bY → cZ. Which of the following can be assumed regarding the order of the reaction? Assume X, Y, and Z are substances and a, b, and c are integer coefficients. |
|
A
|
Order is a + b |
B
|
Order is less than a + b |
C
|
Order is greater than or equal to a + b |
D
|
Order is uncertain from knowing a and b |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 42 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is true regarding the Arrhenius Equation for rate constants? |
|
A
|
it shows that rate is inversely proportional to temperature |
B
|
increasing temperature raises the number of collisions which result in reaction |
C
|
rate is proportional to activation energy |
D
|
activation energy is not a component of the equation |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 43 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following holds true for zero-order reactions? |
|
A
|
They are used as a model for nuclear decay |
B
|
The rates of the reaction depends on reactant concentrations |
C
|
The half-life does not depend on starting concentration |
D
|
The concentration vs. time graph is linear |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 44 |
Go |
Q:
|
An elementary reaction involves the following reaction:
A + A + B → Products
Which of the following reflects the rate law for this reaction? |
|
A
|
rate = k[A][B] |
B
|
rate = k[A]2[B] |
C
|
rate = k[A]2 |
D
|
The answer cannot be determined with the given information. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 45 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given the two benzaldehyde derivatives below, which one will react faster (at the carbonyl carbon) with a nucleophile?
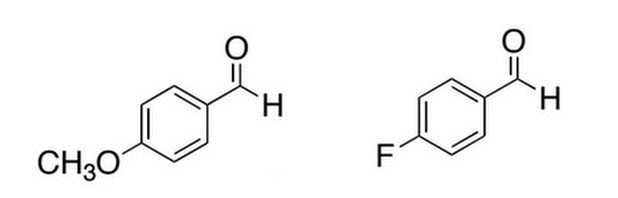 |
|
A
|
The left molecule because the fluoro group is electron-withdrawing, making its carbonyl carbon less electrophilic for addition by a nucleophile
|
B
|
The left molecule because the fluoro group is electron-donating, making its carbonyl carbon less electrophilic for addition by a nucleophile
|
C
|
The right molecule because the fluoro group is electron-withdrawing, making its carbonyl carbon more electrophilic for addition by a nucleophile
|
D
|
The right molecule because the fluoro group is electron-donating, making its carbonyl carbon more electrophilic for addition by a nucleophile
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | Aldehydes and Ketones | Miscellaneous Organic Chemistry | |
|
| 46 |
Go |
Q:
|
Shortly after administration of a drug, its concentration in the blood is 935 μg/L. If the drug elimination follows first order kinetics with a half life of 9 hours, approximately what should the concentration in the blood be after 3 hours? |
|
A
|
850 μg/L |
B
|
740 μg/L |
C
|
470 μg/L |
D
|
510 μg/L |
|
|
|
Tags:
Miscellaneous Biochemistry | Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 47 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following would proceed according to first order kinetics assuming an elementary reaction? |
|
A
|
Linearized glucose becoming cyclized in solution. |
B
|
Glucose and fructose being converted to sucrose by sucrose synthase. |
C
|
The synthesis of glucose-6-phosphate from glucose and ATP. |
D
|
The conversion of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate to fructose bisphosphate. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | Miscellaneous Biochemistry | |
|
| 48 |
Go |
Q:
|
Based on the Arrhenius equation, k = Ae-Ea/(RT), which of the following best describes the temperature-dependence of a reaction? |
|
A
|
As temperature increases, k increases indefinitely. |
B
|
As temperature increases, k increases linearly. |
C
|
As temperature increases, k increases to a maximum value of A. |
D
|
As temperature increases, k increases to a maximum value of 1. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 49 |
Go |
Q:
|
A zero order reaction would have what rate equation? |
|
A
|
Rate = k[A] |
B
|
Rate = k[A][B] |
C
|
Rate = k |
D
|
Rate = k[A]2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 50 |
Go |
Q:
|
An elementary reaction takes place when three molecules of A react in order to form molecule B. Which of the following is the rate law for this reaction? |
|
A
|
k[A]3 |
B
|
3*k[A] |
C
|
k[A] |
D
|
Additional data is required to calculate the order of the reaction. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 51 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular reaction takes place where 2A → B + C is the slow step, and B + 2D → 3E is the fast step. Which of the following is the rate law for this set of reactions? |
|
A
|
rate = k[A]2 |
B
|
rate = k[B][C] |
C
|
rate = k[B][D]2 |
D
|
rate = k[E]3 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 52 |
Go |
Q:
|
A reaction proceeds as follows: X3 → X. Which of the following can be inferred? |
|
A
|
Entropy decreases in the system. |
B
|
The reaction is spontaneous. |
C
|
The reaction is nonspontaneous. |
D
|
The reaction is either spontaneous or nonspontaneous. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 53 |
Go |
Q:
|
The difference in energy between the reactant state and the transition state can be quantified as: |
|
A
|
the enthalpy of the reaction. |
B
|
the entropy of the reaction. |
C
|
the activation energy of the reaction. |
D
|
the activation energy of the reverse reaction. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 54 |
Go |
Q:
|
A reaction takes place with reactants A and B to make product C. When concentration of reactant A doubles, the rate of product formation doubles. When concentration of reactant B doubles, the rate of product formation quadruples. Which of the following expresses the rate equation for this reaction? |
|
A
|
rate = [C]/[A][B] |
B
|
rate = [A][B] |
C
|
rate = [A][B]2 |
D
|
rate = [A]2[B]4 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 55 |
Go |
Q:
|
The Arrhenius equation serves to: |
|
A
|
show dependence of rate constant and temperature. |
B
|
calculate activation energy for chemical reactions. |
C
|
determine concentrations at which reaction rate is maximal. |
D
|
calculate the enthalpy of a reaction. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 56 |
Go |
Q:
|
The half-life of a first-order reaction with a rate constant of 2.1 x 10-3 is approximately: |
|
A
|
30 seconds. |
B
|
300 seconds. |
C
|
3,000 seconds. |
D
|
30,000 seconds. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
| 57 |
Go |
Q:
|
A particular substance is dissolved in water and various energy changes are measured. It is known that heat is absorbed from in this process and the equilibrium constant is measured to be less than 1. What is the sign of the standard entropy change for this process? |
|
A
|
positive |
B
|
negative |
C
|
either positive or negative |
D
|
zero |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | Thermochemistry | |
|
| 58 |
Go |
Q:
|
The rate law for an irreversible chemical reaction depends on which of the following?
I - Temperature
II - Concentration of the Reactants
III - Concentration of the Products
|
|
A
|
I |
B
|
I and II |
C
|
II and III |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemical Kinetics | |
|
|
Questions? We're here to help!
Ask Us
|