|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
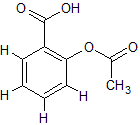
A double replacement reaction occurs in a beaker between reagent X and reagent Y. It is found that water is formed in the reaction. Which of the following cannot be a potential reagent in the reaction? |
|
A
|
HCl |
B
|
NaOH |
C
|
MgCl2 |
D
|
All of the above are potential reagents |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemistry Laboratory Techniques | Miscellaneous Organic Chemistry | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
Ammonium sulfate precipitation involves the addition of the highly-soluble salt ammonium sulfate to raise the ion concentration until proteins differentially precipitate based on their solubility at high ion concentrations. This technique is most similar to: |
|
A
|
mass spectrometry. |
B
|
column chromatography. |
C
|
electrophoresis. |
D
|
PCR. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemistry Laboratory Techniques | Protein Structure and Function | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
Emission spectroscopy is a poor method for identifying organic compounds because: |
|
A
|
the atoms in organic compounds do not have recognizable emission spectra. |
B
|
organic compounds are generally composed of a few different atoms. |
C
|
the emission spectrum of any given organic compound differs each time a reading is taken. |
D
|
organic compounds do not emit light. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemistry Laboratory Techniques | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
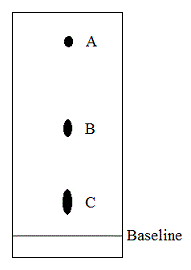
Paper chromatography is run on a wine sample with blots A, B, and C corresponding to lactic, malic, and tartaric acids, respectively. Which of the conclusion regarding the three acids is true based on this information? |
|
A
|
Tartaric acid is the least polar of the acids. |
B
|
Malic acid is more polar than tartaric acid and less polar than lactic acid. |
C
|
Lactic acid is the least polar of the acids. |
D
|
Lactic acid is more polar than malic acid and less polar than tartaric acid. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Intermolecular Forces | Chemistry Laboratory Techniques | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
Under what circumstances would a methyl group appear as a doublet in H1-NMR? |
|
A
|
Deuterium is present on one of the hydrogen atoms in the methyl group. |
B
|
There is only one hydrogen atom attached to the carbon adjacent to the methyl group. |
C
|
There are two hydrogen atoms attached to the carbon adjacent to the methyl group. |
D
|
There are two carbon atoms attached to the carbon adjacent to the methyl group. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemistry Laboratory Techniques | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
A researcher is repeating a colleague's experiment using spectrophotometry and consistently gets absorbance readings for a completed reaction as being higher than reported in the colleague's data. Which of the following would NOT explain higher readings? |
|
A
|
The researcher is using solutions with the analyte being insufficiently diluted. |
B
|
The cuvettes used by the researcher have a longer path length than the cuvettes used by the colleague. |
C
|
The cuvettes used by the researcher have not been properly cleaned. |
D
|
The readings are being taken over a longer period of time. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemistry Laboratory Techniques | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
How would overactive osteoblasts affect the Young's modulus of bone over time? |
|
A
|
The Young's modulus would increase over time. |
B
|
The Young's modulus would decrease over time. |
C
|
The Young's modulus would remain the same over time. |
D
|
The Young's modulus would decrease only if the bone density increased. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemistry Laboratory Techniques | Miscellaneous Physics | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
On a TLC plate, the Rf value is minimized when: |
|
A
|
the analyte is a smaller molecule. |
B
|
the analyte is highly volatile. |
C
|
the analyte is more polar. |
D
|
the analyte is sensitive to UV light. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemistry Laboratory Techniques | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
A solution contains a variety of organic, nonpolar molecules, including strong and weak acids and strong and weak bases. An extraction experiment is held, with a weak acid being added to the solution. Which of the following molecules would be expected to be extracted after draining the aqueous layer of the solution after the weak acid is added? |
|
A
|
weak acids |
B
|
weak bases |
C
|
strong acids |
D
|
strong bases |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemistry Laboratory Techniques | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
Split peaks in NMR suggest: |
|
A
|
the presence of a functional group (e.g., -OH) in a molecule. |
B
|
the presence of chemically equivalent adjacent carbon atoms. |
C
|
the presence of neighboring hydrogen atoms which are not chemically equivalent. |
D
|
the presence of neighboring hydrogen atoms which are chemically equivalent. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemistry Laboratory Techniques | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
Infrared spectroscopy is performed for a molecule and a broad peak is noted at around 3300 cm-1. Which of the following functional groups would be expected within this molecule? |
|
A
|
aromatic |
B
|
amine |
C
|
aldehyde |
D
|
hydroxyl |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemistry Laboratory Techniques | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following types of spectroscopy is mainly used for determination of functional groups on organic molecules? |
|
A
|
IR |
B
|
NMR |
C
|
UV |
D
|
Atomic Emission |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemistry Laboratory Techniques | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) can be used to separate various mixtures. Which of the following is true regarding this type of separation? |
|
A
|
capillary action is an absolute requirement for this type of chromatography |
B
|
plates are typically composed of highly reactive substances that interact with the mixture |
C
|
Rf is a constant value for each substance and is independent of solvent used in the TLC |
D
|
TLC can only be used to separate a mixture of two substances |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemistry Laboratory Techniques | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
Mass spectrometry uses which of the following variables in order to separate molecules? |
|
A
|
mass and density |
B
|
mass and hydrogen atoms |
C
|
mass and charge |
D
|
mass and light polarization |
|
|
|
Tags:
Chemistry Laboratory Techniques | |
|
|
Questions? We're here to help!
Ask Us
|