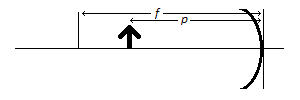|
| 1 |
Go |
Q:
|
An object sits in front of a concave mirror. The object's position is closer to the mirror than the focal point. The image of the object is |
|
A
|
Real and upright |
B
|
Real and inverted |
C
|
Virtual and upright |
D
|
Virtual and inverted |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 2 |
Go |
Q:
|
A mirror with a focal length of -2.5 m. An object is placed 7.5 m in front of the mirror. Where will the image of the object show up? |
|
A
|
1.9 m behind the mirror |
B
|
1.9 m in front of the mirror |
C
|
0.33 m behind the mirror |
D
|
0.33 m in front of the mirror |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 3 |
Go |
Q:
|
Myopia is a condition in which the focal point of the lens of the eye is in front of the retina. This results in a distorted image. In order to correct this condition, an individual should use a _______ in order to move the focal point _______. |
|
A
|
converging lens, on the retina |
B
|
diverging lens, on the retina |
C
|
converging lens, behind the retina |
D
|
diverging lens, behind the retina |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 4 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following systems is incapable of producing a virtual image? |
|
A
|
Concave mirror |
B
|
Convex mirror |
C
|
Convex lens |
D
|
None of the above |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 5 |
Go |
Q:
|
The focal length of a mirror is 2 meters. What is its radius of curvature? |
|
A
|
0.25 m |
B
|
0.5 m |
C
|
2 m |
D
|
4 m |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 6 |
Go |
Q:
|
Given a mirror or lens, assume that a "real" image is on the same side as the object. "Virtual" refers to the other side of the lens/mirror that is "inside" the lens or mirror. Given this nomenclature, for an object in focus, a concave mirror makes a:
|
|
A
|
real, upright image |
B
|
virtual, upright image |
C
|
real, inverted image |
D
|
virtual, inverted image |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 7 |
Go |
Q:
|
An upright object is located on the axis of a convex lens, 6 focal lengths from the lens center. An inverted image is seen at a distance of 3/2 focal lengths on the opposite side of the lens. Calculate the ratio of the image to object height.
|
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 8 |
Go |
Q:
|
What is the focal length of a concave mirror with a radius of 1 m? |
|
A
|
0.25 m |
B
|
0.5 m |
C
|
1 m |
D
|
2 m |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 9 |
Go |
Q:
|
The reflected image in a convex mirror will be |
|
A
|
virtual and upright |
B
|
virtual and inverted |
C
|
real and upright |
D
|
real and inverted |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 10 |
Go |
Q:
|
If the index of refraction is equal for two bordering media of differing densities, the angle of refraction of light passing from one medium to the other will be |
|
A
|
greater than the incident angle if the first medium is denser than the second |
B
|
equal to the incident angle |
C
|
less than the incident angle if the first medium is denser than the second |
D
|
the answer cannot be determined with the given information |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 11 |
Go |
Q:
|
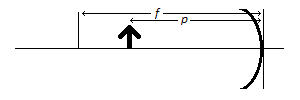
If an object sits inside the focal length of a concave mirror as in the diagram above, the image formed will be |
|
A
|
virtual and upright |
B
|
virtual and inverted |
C
|
real and upright |
D
|
real and inverted |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 12 |
Go |
Q:
|
As light passes from one medium into another, its angle of refraction will always be the same as the incident angle if |
|
A
|
the index of refraction of the first medium is 1 and the second medium is greater than 1 |
B
|
the index of refraction of the second medium is 1 and the first medium is greater than 1 |
C
|
the index of refraction of both media is greater than 1 |
D
|
the index of refraction of both media is the same |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 13 |
Go |
Q:
|
An object is placed infinitely far away from a biconvex lens. Which of the following holds true? |
|
A
|
The lens will act exactly the same as a biconvex lens |
B
|
The image will appear on the same side of the lens as the object |
C
|
The image will appear exactly the focal length in front of the lens |
D
|
Light will not converge and thus no image will be formed |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 14 |
Go |
Q:
|
The focal length of concave mirror refers to |
|
A
|
a distance away from the mirror where parallel rays will converge |
B
|
a value double the radius of curvature |
C
|
whether a mirror is concave or convex |
D
|
a value which increases with increasing convergent strength of the mirror |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 15 |
Go |
Q:
|
The index of refraction for a glass ceiling over a football stadium is found to be 2.5. It is approximately 5 m thick. How long does it take light to cross this glass ceiling? |
|
A
|
5 * 10-7 seconds |
B
|
4 * 10-8 seconds |
C
|
1 * 10-8 seconds |
D
|
5 * 10-9 seconds |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 16 |
Go |
Q:
|
As a ray of light passes from one medium into another, the angle of the ray of light changes. Assuming no dispersion, if the wavelength of that ray of light is increased, the angle of refraction will |
|
A
|
decrease. |
B
|
remain the same. |
C
|
increase. |
D
|
increase or decrease, depending on whether there is an increase or decrease in the index of refraction. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 17 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following correctly describes the image formed by a biconvex lens where the distance of the object to the lens is less than the focal length of the lens? |
|
A
|
virtual and upright |
B
|
virtual and inverted |
C
|
real and upright |
D
|
real and inverted |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 18 |
Go |
Q:
|
A biconvex lens is used to magnify the image of an object. When the lens is held at a distance of 1 cm from the object, an image forms that is 5 cm from the lens. What is the focal length of the lens? |
|
A
|
1/5 cm |
B
|
5/6 cm |
C
|
6/5 cm |
D
|
5 cm |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 19 |
Go |
Q:
|
A biconvex lens can produce a virtual image if which of the following is true? |
|
A
|
The image is inverted. |
B
|
The object is at infinity. |
C
|
The image is formed at the focal length. |
D
|
The object is inside the focal length of the lens. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 20 |
Go |
Q:
|
Aurora, called the Northern Lights in the northern hemisphere, result partly from nitrogen in the upper atmosphere. The nitrogen atoms are either ionized or excited, and emit light when returning to their ground state. Depending on whether the nitrogen is ionized or excited, the colors blue or red are emitted. Which of the following accurately describes the relationship between color and energy state? |
|
A
|
Ionized nitrogen returning to ground state produces red light while excited nitrogen returning to ground state emits blue light because there is a greater energy difference between ionization and ground than excitation and ground. |
B
|
Ionized nitrogen returning to ground state produces red light while excited nitrogen returning to ground state emits blue light because there is a greater energy difference between excitation and ground than ionization and ground. |
C
|
Ionized nitrogen returning to ground state produces blue light while excited nitrogen returning to ground state emits red light because there is a greater energy difference between excitation and ground than ionization and ground. |
D
|
Ionized nitrogen returning to ground state produces blue light while excited nitrogen returning to ground state emits red light because there is a greater energy difference between ionization and ground than excitation and ground. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 21 |
Go |
Q:
|
A student looks into a mirror and sees her reflection is upright. Which of the following mirrors could she be observing?
I. concave mirror
II. convex mirror
III. flat mirror |
|
A
|
III only |
B
|
II and III only |
C
|
I and II only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 22 |
Go |
Q:
|
A doctor is rushing through the hospital hallway to the emergency room and is approaching a corner. In order to avoid a collision, the doctor looks at the convex safety mirror in the corner of the hallway. Describe the image in the mirror as the doctor approaches the corner. |
|
A
|
Real, Inverted |
B
|
Virtual, Inverted |
C
|
Real, Upright |
D
|
Virtual, Upright |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 23 |
Go |
Q:
|
A laboratory shines a single beam of light into a fluid at an angle of 30°. Assuming the refractive index of air is 1, and the beam of light refracts at an angle of 60°, what is the refractive index of the unknown fluid?
|
|
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 24 |
Go |
Q:
|
Lee sees his brother's car parked across the street. His sister's car is parked next to him. Because his brother's car is some distance away, it appears smaller than his sister's car. Lee's brain can determine the approximate distance and size of the car by using which visual cue?
I. Accommodation
II. Convergence
III. Stereopsis |
|
A
|
I and II only |
B
|
II and III only |
C
|
I and III only |
D
|
I, II, and III |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | Sensory Processing | |
|
| 25 |
Go |
Q:
|
A lens forms an image at 2 cm when focusing an image that is 15 cm away. What is the focal length of the lens? |
|
A
|
17/30 cm |
B
|
30/17 cm |
C
|
1/17 cm |
D
|
17 cm |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 26 |
Go |
Q:
|
A light source is placed near a diverging lens. For which placement would a real image be formed? |
|
A
|
At the focal length |
B
|
At a distance of twice the focal length |
C
|
At a distance half the focal length |
D
|
A real image can never be formed |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 27 |
Go |
Q:
|
An object is placed 4m away from a giant converging lens. The image that is formed by this lens is a distance of 6m from the object. What is the focal length of the lens? |
|
A
|
12/5 |
B
|
5/12 |
C
|
4/3 |
D
|
3/4 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | Quantitative Skills | |
|
| 28 |
Go |
Q:
|
A person stands in front of a converging lens at a distance D. The focal length for the lens is F. If D is less than F, what type of image of the person is formed? |
|
A
|
Real and upright |
B
|
Real and inverted |
C
|
Virtual and upright |
D
|
Virtual and inverted |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 29 |
Go |
Q:
|
A beam of light traveling through air is first refracted by a lens and then reflected by an imperfect mirror (i.e., some of the energy from the photons are absorbed by the mirror). Which of the following remains constant at the start and end of the experiment?
I. wavelength
II. frequency
III. speed |
|
A
|
I and II only |
B
|
III only |
C
|
I, II, and III |
D
|
II and III only |
|
|
|
Tags:
Electromagnetics | Optics | |
|
| 30 |
Go |
Q:
|
Of the following choices, which is NOT most likely to cause diffraction to occur when light passes through the setup? |
|
A
|
Wide slit |
B
|
Narrow slit |
C
|
Pinhole |
D
|
Glass |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 31 |
Go |
Q:
|
If a virtual image is being projected by a mirror, the mirror: |
|
A
|
must be concave only. |
B
|
must be convex only. |
C
|
can be either concave or convex. |
D
|
cannot be flat. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 32 |
Go |
Q:
|
When the lens of the eye flattens when focusing on an image, it functionally serves to: |
|
A
|
decrease the focal length of the eye. |
B
|
increase the focal length of the eye. |
C
|
invert the image on to the retina. |
D
|
decrease the amount of light entering the posterior compartment of the eye. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 33 |
Go |
Q:
|
An object is placed 5 cm in front of a lens and an image is formed 10 cm in behind the lens. Which of the following is equivalent to the power of the lens? |
|
A
|
0.43 m-1 |
B
|
3.33 m-1 |
C
|
10 m-1 |
D
|
30 m-1 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 34 |
Go |
Q:
|
Refractive index for an optical medium is defined as: |
|
A
|
speed of light through a vacuum composed of this optical medium. |
B
|
the velocity at which light would escape the medium. |
C
|
ratio of speed of light in a vacuum and speed of light through the medium. |
D
|
fractional wavelength decrease of a light traveling through this medium when compared to a vacuum. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 35 |
Go |
Q:
|
For an object placed beyond the focal length of a concave lens, which of the following image types will be produced? |
|
A
|
virtual, upright |
B
|
virtual, inverted |
C
|
real, upright |
D
|
real, inverted |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 36 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following waves would be expected to have the shortest wavelength? |
|
A
|
microwaves |
B
|
visible light |
C
|
ultraviolet light |
D
|
infrared |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 37 |
Go |
Q:
|
Light from a flashlight is typically: |
|
A
|
horizontally polarized. |
B
|
vertically polarized. |
C
|
circularly polarized. |
D
|
unpolarized. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 38 |
Go |
Q:
|
Total internal reflection: |
|
A
|
takes place when all light from one medium refracts as it enters a different medium. |
B
|
is an identical term to critical angle. |
C
|
takes place when light moves from a medium with higher index of refraction to a lower index of refraction. |
D
|
is only a term relevant to light traveling through water. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 39 |
Go |
Q:
|
A lens of diameter 4cm and a focal length 25cm would be expected to have a power of: |
|
A
|
1 m-1. |
B
|
4 m-1. |
C
|
0.04 m-1. |
D
|
0.1 m-1. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 40 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following is capable of producing a real image?
I. concave lens
II. concave mirror
III. convex lens
IV. convex mirror
|
|
A
|
I and IV only |
B
|
II and IV only |
C
|
II and III only |
D
|
I, II, III, and IV |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 41 |
Go |
Q:
|
A 3m object is placed 65m away from a convex lens with focal length 10cm. How far from the lens will the lens generate the image of the object? |
|
A
|
0.1 m |
B
|
0.67 m |
C
|
1.2 m |
D
|
1.4 m |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 42 |
Go |
Q:
|
The diopter has which of the following units? |
|
A
|
1/length |
B
|
1/length2 |
C
|
length |
D
|
length2 |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 43 |
Go |
Q:
|
Lens power has a units of: |
|
A
|
m |
B
|
m-1/2 |
C
|
m-1 |
D
|
unitless |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 44 |
Go |
Q:
|
An object is placed in front of a convex lens at a distance half the length of the focal length. The image produced of the object would be: |
|
A
|
virtual and upright. |
B
|
virtual and inverted. |
C
|
real and upright. |
D
|
real and inverted. |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 45 |
Go |
Q:
|
For a flat mirror, the center of curvature is located at: |
|
A
|
0 |
B
|
1 meter away from the mirror |
C
|
greater than one meter away from the mirror but is non-infinite |
D
|
infinity |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 46 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following colors has the lowest wavelength? |
|
A
|
indigo |
B
|
green |
C
|
yellow |
D
|
red |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 47 |
Go |
Q:
|
Which of the following mirror/lens types are able to produce a virtual image?
I. convex lens
II. convex mirror
III. concave mirror |
|
A
|
I only |
B
|
II and III only |
C
|
I and III only |
D
|
I, II and III only |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
| 48 |
Go |
Q:
|
An object is placed 5 m from a convex lens and an image is produced 20 m away from the lens on the opposite side as the object. What is the focal length of this lens? |
|
A
|
15 m |
B
|
4 m |
C
|
0.25 m |
D
|
25 m |
|
|
|
Tags:
Optics | |
|
|
Questions? We're here to help!
Ask Us
|